Application of AI in Banking
The application of AI in banking refers to how banks use artificial intelligence to improve services, boost security, and make smarter decisions. AI helps in detecting fraud, offering 24/7 customer support through chatbots, automating tasks like loan approvals, and analyzing data to personalize banking experiences, which also helps banks manage risks more effectively and speed up transaction processing. In simple terms, it makes banking faster, more secure, and convenient for both customers and financial institutions.
Whether it’s saving time or preventing fraud, the application of AI in banking is transforming how financial institutions operate today.
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence in Banking
In the rapidly evolving world of finance, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming how banks operate, make decisions, and interact with customers. From automating routine tasks to predicting financial risks with precision, AI has emerged as a game-changer in the banking industry.
But what exactly is Artificial Intelligence in banking, and why is it gaining so much attention?
What is Artificial Intelligence in Banking?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) means using computer programs or algorithms that mimic human thinking—like learning, analyzing, solving problems, and making smart decisions.
In banking, this means using AI-powered systems to:
- Analyze large amounts of customer data
- Predict financial behaviors and market trends.
- Prevent fraud and assess risk.
- Provide personalized banking experiences.
- Automate customer service and back-office operations
AI in banking is not just about robots replacing human jobs—it’s about enhancing human intelligence and enabling smarter, faster, and safer financial services.
How AI is Reshaping the Financial Services Industry
Over the last decade, global banks and financial institutions have invested heavily in AI. A 2023 report by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) highlighted AI as a strategic priority for digital banking transformation. According to McKinsey, AI has the potential to add nearly $1 trillion in value annually to the global banking sector by boosting performance and efficiency.
Here’s how AI is making an impact:
Area | AI Impact |
Customer Service | 24/7 chatbots, voice assistants, and personalized recommendations |
Fraud Detection | Real-time transaction monitoring and suspicious activity alerts |
Risk Management | AI-powered risk scoring, underwriting, and loan approval |
Operations | Automation of repetitive processes, reducing cost and error |
Investment & Wealth | Robo-advisors and algorithmic trading platforms |
Why Banks Are Investing in AI: Global and Indian Context
AI is not just a trend—it’s a competitive advantage. Here’s why banks around the world, including in India, are embracing it:
Global Perspective:
- Banks like JP Morgan, HSBC, and Bank of America use AI for everything from customer service to fraud detection.
- AI is helping banks manage increasing data complexity, cyber threats, and customer demands for personalization.
Indian Perspective:
- Indian banks such as SBI, HDFC, ICICI, and Yes Bank are leveraging AI to improve customer support, detect fraud, and enable digital lending.
- Examples such as SBI’s YONO app and HDFC’s EVA virtual assistant highlight how banks are already using AI to enhance customer service and operations.
- RBI is pushing for “responsible AI” frameworks and has proposed data governance standards for financial AI systems.
Key Statistics That Show AI’s Impact on Banking
- 75% of banking executives say AI will be critical to their business success in the next 2 years (Source: Accenture)
- Over 60% of Indian banks have adopted some form of AI or ML-based technology (Source: NASSCOM)
- AI-based fraud detection can reduce false positives by up to 80% and save millions annually.
- AI-powered chatbots can manage more than 80% of everyday customer questions, which helps cut down on service costs and improves response speed.
Summary of the Introduction
Artificial Intelligence is no longer a futuristic concept in banking—it’s here and growing fast. From improving customer satisfaction to minimizing risk and fraud, AI is helping banks become more efficient, secure, and future-ready.
In the next sections, we’ll explore the core applications, real-world use cases, benefits, risks, and the future potential of AI in banking.

Strategic Applications of AI in Banking
As the banking industry becomes increasingly data-driven, AI technologies are at the heart of digital transformation. They enable banks to not only streamline operations but also provide smarter, safer, and more personalized experiences to customers.
Now, let’s dive into some of the most powerful and practical ways AI is transforming the banking sector today.
1. AI in Risk Management and Assessment
Risk management is a critical function in banking. With rising complexities in global finance, traditional risk models fall short in identifying emerging threats. AI fills this gap by offering:
Key Applications:
- Real-Time Risk Scoring: AI models assess borrower creditworthiness by analyzing structured and unstructured data (like social media, spending habits).
- Early Warning Systems: ML algorithms detect signs of financial stress or market volatility.
- Portfolio Risk Monitoring: AI tools track changes in portfolios and suggest adjustments to reduce exposure.
Benefits:
- Faster, more accurate decisions
- Reduced Non-Performing Assets (NPAs)
- Better compliance with risk regulations
Example:
- ICICI Bank uses AI-based credit models for faster loan processing and risk profiling.
2. AI in Fraud Detection and Prevention
Fraud is a growing threat, costing the global financial industry billions of dollars annually. AI enhances fraud prevention through:
Key Applications:
- Anomaly Detection: AI continuously scans banking transactions and instantly detects unusual or suspicious patterns that may indicate fraud.
- Behavioral Analysis: AI learns user behavior and detects deviations (e.g., logging in from a new location/device).
- Pattern Recognition: AI detects complex fraud networks and uncovers hidden links in money laundering activities by spotting recurring transaction patterns.
Benefits:
- 24/7 fraud protection
- Reduction in false positives
- Faster incident response
Example:
- HDFC Bank uses AI-powered systems to detect unusual spending patterns and block unauthorized transactions instantly.
3. AI in Credit Scoring and Underwriting
Conventional credit scoring mainly depends on a borrower’s CIBIL score and past income records to assess creditworthiness.
Key Applications:
- Alternative Data Use: AI analyzes non-traditional data like utility bills, digital behavior, and mobile recharge history.
- ML Models: Predict repayment capability with greater accuracy than rule-based systems.
- Dynamic Scoring: Real-time score updates based on financial activity.
Benefits:
- Inclusion of first-time borrowers
- Faster loan approvals
- More accurate risk prediction
Example:
- Fintechs like KreditBee and ZestMoney use AI-based models to offer credit to users without a credit history.
4. AI in Predictive Analytics for Market Trends
AI enables banks to forecast market changes and customer behavior with precision.
Key Applications:
- Churn Prediction: Identify customers likely to leave and retain them with timely offers.
- Investment Insights: AI-powered advisory for wealth management.
- Demand Forecasting: Predict credit needs, deposits, and market interest.
Data Sources Used:
- Social media trends
- Transaction history
- Macroeconomic indicators
Example:
- Yes Bank uses AI to analyze market sentiment for better investment decisions.
5. AI in Customer Service Automation
Customer expectations have evolved. They want instant, personalized service. AI enables banks to deliver just that:
Key Applications:
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Handle FAQs, KYC queries, and balance checks.
- Voice Assistants: Integrate with mobile apps for natural-language banking.
- Smart FAQs & Dynamic Help Centers: AI tailors answers to individual user behavior.
Benefits:
- 24/7 availability
- Reduced workload on human agents
- Cost savings
Example:
- HDFC Bank’s EVA virtual assistant has handled more than 5 million customer queries, delivering responses with an impressive 85% accuracy rate.
6. AI in Personalized Banking Services
AI helps banks treat each customer as a “segment of one” by offering hyper-personalized experiences.
Key Applications:
- Product Recommendations: AI suggests relevant banking products by analyzing each customer’s habits, preferences, and financial objectives.
- Custom Alerts and Offers: Tailored promotions using predictive AI.
- Spending Insights: Categorized analysis with budgeting suggestions.
Benefits:
- Increased customer loyalty
- Higher product adoption
- Enhanced satisfaction
Example:
- SBI YONO app uses AI to show personalized product suggestions and lifestyle offers.
Summary of Strategic Applications
From risk management to customer engagement, AI is embedded across all major banking functions. These intelligent systems not only boost efficiency but also create safer, faster, and more inclusive financial ecosystems.
The Rise of Generative AI in Banking
As the banking sector continues to adopt automation and intelligent systems, a powerful new branch of AI is emerging at the forefront — Generative AI. Unlike traditional AI, which mainly performs tasks like classification or prediction, Generative AI (GenAI) is capable of producing entirely new content—such as text, images, reports, and synthetic data.
In banking, this unlocks a new world of possibilities for efficiency, creativity, and personalized experiences.
What is Generative AI in Banking?
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that creates new content or data by learning from existing patterns and information.
In banking, this means:
- Auto-generating reports, summaries, and documents
- Creating realistic synthetic financial data for training/testing
- Automating customer communication with human-like responses
- Enhancing risk and compliance documentation
Popular tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and Google Gemini are now being integrated into financial services for both internal and customer-facing tasks.
Key Applications of Generative AI in Banking
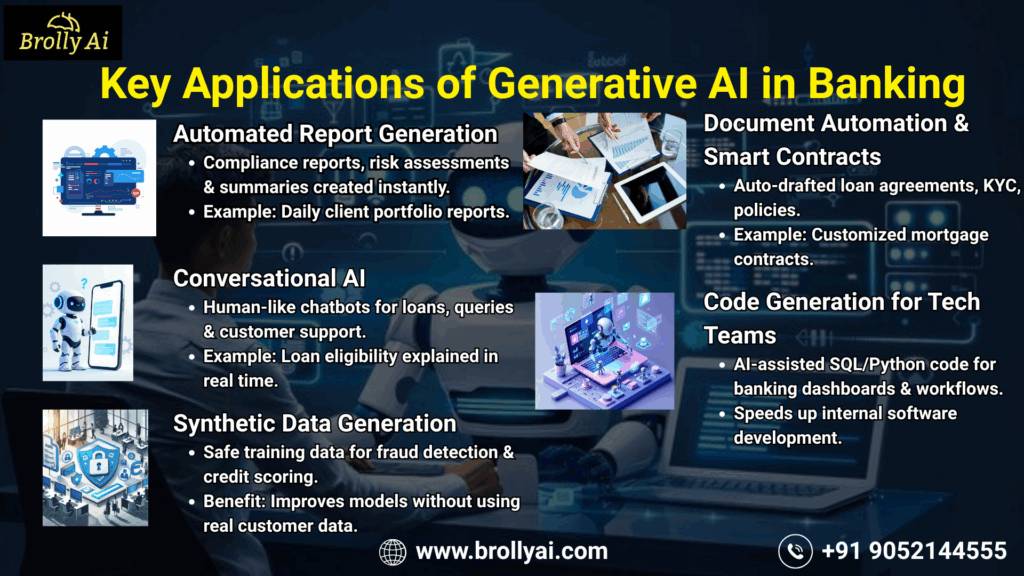
1. Automated Report Generation
- Generative AI can create compliance reports, risk assessments, and financial summaries without human intervention.
- It eliminates hours of manual effort while ensuring that all generated content remains consistent, accurate, and ready for use.
Example: An investment bank uses GenAI to generate client portfolio reports daily.
2. Conversational AI for Human-like Customer Service
- Unlike traditional rule-based bots, GenAI can generate natural-sounding responses to complex questions.
- It recognizes the user’s context and responds in a tone that feels natural, personalized, and appropriate to the conversation.
Example: A GenAI-powered chatbot helps customers understand loan eligibility by analyzing their transaction history in real time.
3. Synthetic Data Generation
- Useful for banks where real customer data is sensitive or restricted.
- GenAI can create simulated data for training fraud detection models or credit scoring systems.
Benefit: Enhances AI model accuracy without compromising data privacy.
4. Document Automation & Smart Contracts
- Draft loan agreements, KYC forms, and policy documents automatically.
- Integrates with banking APIs to pull customer data and fill templates.
Example: A bank generates customized mortgage contracts based on client profile inputs.
5. Code Generation for Internal Tech Teams
- Fintech and IT teams use GenAI tools to speed up the development of internal banking software.
- It assists developers by producing Python or SQL code for building dashboards, running data analysis, and managing internal workflows.
Benefits of Generative AI in Banking
Benefit | Description |
Faster Document Creation | Saves time on manual writing and formatting |
Improved Compliance | Generates consistent, regulator-ready documents |
Scalable Personalization | Delivers custom messages at scale for marketing or service |
Privacy-Friendly Testing | Uses synthetic data to train models securely |
Better Customer Experience | Provides smarter, emotionally aware interactions |
Challenges of Generative AI in Banking
While powerful, GenAI also brings unique concerns:
- Hallucination: Sometimes generates incorrect or fictitious information
- Data Security: Sensitive inputs need encryption and compliance layers
- Bias & Fairness: AI outputs can reflect biases from training data
- Regulatory Oversight: Need for clear guidelines on the use of GenAI in financial operations
Indian and Global Adoption
- Yes Bank is experimenting with GenAI-powered internal tools for reporting.
- Axis Bank is exploring the use of conversational Generative AI tools to deliver tailored financial guidance and support in wealth management.
- Globally, JPMorgan has developed “IndexGPT,” a GenAI tool to select investments for clients.
Summary of the Rise of Generative AI
Generative AI is not replacing traditional AI — it’s augmenting it with capabilities that bring creativity, automation, and personalization to a new level. For banks, GenAI offers a strategic advantage in creating faster, smarter, and more secure financial services.
Responsible and Ethical AI in Financial Services
As banks race to adopt Artificial Intelligence for competitive advantage, ethical use and responsible governance have become critical concerns. Financial institutions handle sensitive data, influence credit access, and manage national-scale economies — making the ethical deployment of AI a necessity, not an option.
What is Responsible AI in Banking?
Responsible AI in banking means building and using AI systems that are designed with fairness, safety, transparency, and accountability in mind.
- Transparent: Clear in how decisions are made
- Fair: Free from bias or discrimination
- Secure: Protecting user data and privacy.
- Accountable: Governed by clear regulations and human oversight
In banking, Responsible AI ensures that credit decisions, fraud alerts, and customer profiling are made fairly and reliably — especially for vulnerable customers.
Why is Ethical AI Important in Financial Services?
Banks are now using AI to make decisions that were once made by humans, such as:
- Who gets a loan?
- What interest rate should be offered?
- Is a transaction fraudulent?
- Is a customer financially risky?
If the underlying AI models are biased or opaque, they can:
- Discriminate against certain demographics
- Deny legitimate access to financial services.
- Cause reputational damage and regulatory penalties.
Hence, ethical guardrails are essential.
Common Ethical Challenges in AI for Banking
Challenge | Description |
Bias in Data | Training data may reflect social or economic bias, leading to unfair decisions |
Black Box Models | Some AI algorithms (e.g., deep learning) are hard to interpret or explain |
Data Privacy Risks | Sensitive customer data must be protected from misuse or leakage |
Lack of Regulation | Rapid AI development outpaces legal and regulatory frameworks |
Global Guidelines for Ethical AI
- OECD’s AI Principles encourage countries to adopt AI that respects human values, ensures openness, and holds systems accountable for their actions.
- The EU AI Act (2024) categorizes AI tools by risk level and sets firm regulations, especially for high-risk areas like finance and credit decision-making.
- FATF Guidance: For using AI in anti-money laundering (AML) compliance.
Responsible AI Initiatives in India
RBI’s Push for Ethical AI
Recognizing AI’s increasing role in finance, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is actively guiding banks to adopt ethical and transparent AI practices.
- Fairness in credit algorithms
- Data governance and model validation
- Transparency in AI decision-making
RBI has also recommended “explainable AI” (XAI) models — especially in underwriting, fraud detection, and KYC.
Data Privacy Law: India’s 2023 Data Protection Act ensures banks handle customer data responsibly, with user consent and privacy rights at the core.
- Governs how banks collect, store, and use customer data
- Mandates consent and rights to data access/deletion
- Requires banks to appoint Data Protection Officers (DPOs) and report breaches
Best Practices for Responsible AI in Banking
- Bias Testing: Regularly audit models for demographic bias
- Explainable AI: Use interpretable models for high-risk decisions
- Data Minimization: Only collect necessary data for analysis
- Human-in-the-Loop: Keep critical decisions under human oversight
- Governance Framework: Create internal AI ethics boards or audit systems
Real-World Example: Responsible AI in Action
Axis Bank conducts fairness checks on its AI-driven credit decision systems to ensure that customers are treated equally and without algorithmic bias.
ICICI Bank uses a hybrid approach — combining AI predictions with human review for complex loan approvals.
Summary of Ethical AI in Banking
As AI becomes deeply embedded in banking operations, responsible AI is the foundation for trust. Ethical use of AI helps banks not only avoid regulatory trouble but also build stronger relationships with customers and the public.
By aligning with global and Indian standards, banks can ensure their AI systems are fair, explainable, and accountable.
Benefits of AI in Banking
Artificial Intelligence is not just a futuristic tool — it’s a core driver of business transformation in banking today. From front-end customer experiences to back-end operations, AI is delivering significant value across all layers of the banking ecosystem.
Let’s break down the top benefits that AI brings to the banking industry.
1. Improved Operational Efficiency
AI automates repetitive, time-consuming tasks such as:
- Document verification
- KYC (Know Your Customer) processing
- Loan application screening
- Email responses and query sorting
This leads to:
- Faster turnaround times
- Lower labor costs
- Reduced human error
Example: Banks using AI-powered Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can process thousands of forms daily without manual intervention.
2. Enhanced Fraud Detection and Security
AI systems monitor millions of transactions in real-time to detect unusual or suspicious activities.
Benefits include:
- Immediate fraud alerts and blocking
- Better protection against phishing and cyberattacks
- Behavioral analysis to catch insider threats
Example: AI models helped one Indian private bank reduce credit card fraud losses by over 40% in 12 months.
3. Personalized Customer Experiences
AI enables banks to gain deep insights into each customer’s habits, financial goals, and preferences for more personalized service.
It enables:
- Hyper-personalized product recommendations
- Customized investment portfolios
- Smart notifications and alerts
- Real-time customer insights
Example: SBI’s YONO app uses AI to suggest relevant financial products and lifestyle offers.
4. Faster and Smarter Decision-Making
With real-time analytics and predictive models, AI helps banks:
- Approve loans quickly
- Detect default risks early.
- Adjust product pricing dynamically.
- Make investment decisions backed by data.
This reduces delay in decisions and improves overall agility.
5. Scalability and 24/7 Service
AI systems don’t sleep or take breaks. Banks can:
- Serve customers round the clock via AI chatbots and voice assistants
- Expand operations without proportionally increasing costs.
- Handle large transaction volumes without service drop.
Example: HDFC’s EVA chatbot handles over 100,000 queries a day, reducing pressure on human agents.
6. Better Risk Management
AI enhances risk models with:
- Accurate credit scoring
- Real-time monitoring of borrower behavior
- Fraud detection in loan applications
- Stress testing and scenario simulation
This helps banks minimize defaults and manage market volatility more effectively.
7. Cost Reduction
By automating tasks and improving accuracy, AI helps banks:
- Cut down operational costs
- Reduce compliance penalties
- Avoid losses from fraud or defaults.
According to a Deloitte report, AI can reduce banking costs by up to 25% over the next 5 years.
8. Competitive Advantage and Innovation
AI enables banks to:
- Launch new digital products faster
- Offer services tailored to tech-savvy users
- Gain insights from big data to stay ahead of the market trends.
Banks that adopt AI early position themselves as innovators and market leaders.
9. Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
AI helps with:
- Real-time compliance checks
- Automated regulatory filings
- Risk and audit trail documentation
- Anti-money laundering (AML) pattern recognition
This minimizes the chance of regulatory penalties and makes audit processes quicker and more efficient.
10. Business Continuity and Disaster Resilience
AI can:
- Detect cyber threats before they spread
- Redirect workload to backup systems.
- Support continuity planning through simulations.
Especially post-COVID, AI is seen as a critical tool for resilient digital banking.
Summary of Benefits
Area | Key Benefit |
Operations | Efficiency, speed, and cost savings |
Customers | Personalization, 24/7 service, better experiences |
Risk | Enhanced fraud detection, credit risk evaluation |
Strategy | Competitive edge, innovation, growth enablement |
Compliance | Real-time regulatory alignment and reporting |
AI is no longer a supporting tool — it’s a core enabler of next-gen banking. Banks that use AI strategically not only serve customers better but also operate smarter, faster, and more securely.

Challenges, Risks, and Limitations of AI in Banking
While Artificial Intelligence offers numerous benefits to the banking industry, its adoption is not without hurdles. From data privacy concerns to regulatory risks, banks must navigate several technical, ethical, and operational challenges to implement AI responsibly and effectively.
Here are the key limitations and risks that financial institutions need to consider:
1. Data Privacy and Security Risks
AI relies on massive volumes of sensitive data — including customer transactions, personal details, credit history, and even location data. This creates a major risk:
- Data breaches due to improper access controls
- Unauthorized use of customer data without consent
- Vulnerabilities in third-party AI tools or APIs
India’s Data Protection Law (DPDP Act 2023) requires banks to protect customer data with strict consent, purpose limitation, and security mechanisms.
2. Bias and Discrimination in AI Models
AI algorithms learn from data — but if that data is biased, the decisions will be too.
Example issues:
- AI is denying loans more often to women or marginalized communities
- Higher risk scores for certain regions or income groups
- Biased chatbot responses based on limited training data
Banks must regularly audit their AI systems to ensure fairness, diversity, and inclusion.
3. Lack of Explainability (Black Box Problem)
Many advanced AI models — especially deep learning — function as “black boxes” where it’s difficult to understand how decisions are made.
This creates issues with:
- Regulatory compliance (e.g., RBI mandates explainable models)
- Customer trust
- Internal audits and validation
Banks need Explainable AI (XAI) solutions that provide clear, interpretable reasoning for decisions.
4. Integration with Legacy Systems
Most traditional banks still run on legacy IT infrastructure, which isn’t always compatible with modern AI systems.
Challenges include:
- High cost of upgrading systems
- Lack of APIs for AI integration
- Data silos and fragmented architecture
This slows down AI deployment and reduces effectiveness.
5. Regulatory and Compliance Complexities
AI in banking is evolving faster than the laws that govern it. Key concerns:
- No universal AI regulations — compliance differs by country
- AML, KYC, and lending decisions require explainability and fairness
- Real-time AI systems may lack clear audit trails.
Banks must work with regulators to co-create responsible AI guidelines.
6. High Implementation Costs
While AI can reduce costs over time, initial investments can be significant:
- Hiring AI talent
- Data cleaning and infrastructure setup
- Model training and testing
- Regulatory compliance spending
This can be a barrier for smaller banks and cooperative institutions.
7. Over-Reliance on AI Systems
AI can only perform well if it’s trained on accurate, diverse, and unbiased data—poor data leads to poor decisions.
- Human oversight may decrease.
- Critical judgment may be lost in favor of automation.
- Unexpected model failures could go unnoticed.
For important decisions, banks should always keep human oversight in place to review and validate AI-generated outcomes.
8. Ethical and Moral Dilemmas
AI introduces moral questions:
- Should AI decide who qualifies for a loan?
- Is it ethical to use AI for emotional manipulation in marketing?
- Can customers opt out of AI-based profiling?
These questions must be addressed in an AI ethics policy.
Summary of Challenges
Challenge Area | Key Risk |
Data | Privacy breaches, data misuse |
Models | Bias, lack of explainability |
Systems | Legacy integration issues |
Regulation | Unclear or evolving guidelines |
Ethics | Moral concerns, human dignity |
Costs | High initial investment, talent shortage |
How Banks Can Overcome These Challenges
- Use Explainable AI tools for high-risk decisions.
- Conduct regular audits for bias and fairness.
- Strengthen cybersecurity and data governance.
- Collaborate with regulators to co-develop guidelines.
- Upskill employees to work alongside AI
- Pilot projects first, then scale gradually
AI offers huge potential, but its true value comes from using it carefully, ethically, and with proper checks in place. By understanding and mitigating these challenges, banks can unlock AI’s full potential while preserving trust, compliance, and transparency.
The Future of AI in Banking: Trends and Innovations Shaping the Next Decade
Artificial Intelligence is not just transforming banking today — it is laying the foundation for the next generation of financial services. The future of AI in banking is exciting, as rapid innovation, regulatory alignment, and digital-first customer behaviors continue to push the boundaries.
Here are the key trends and future possibilities in AI-powered banking:
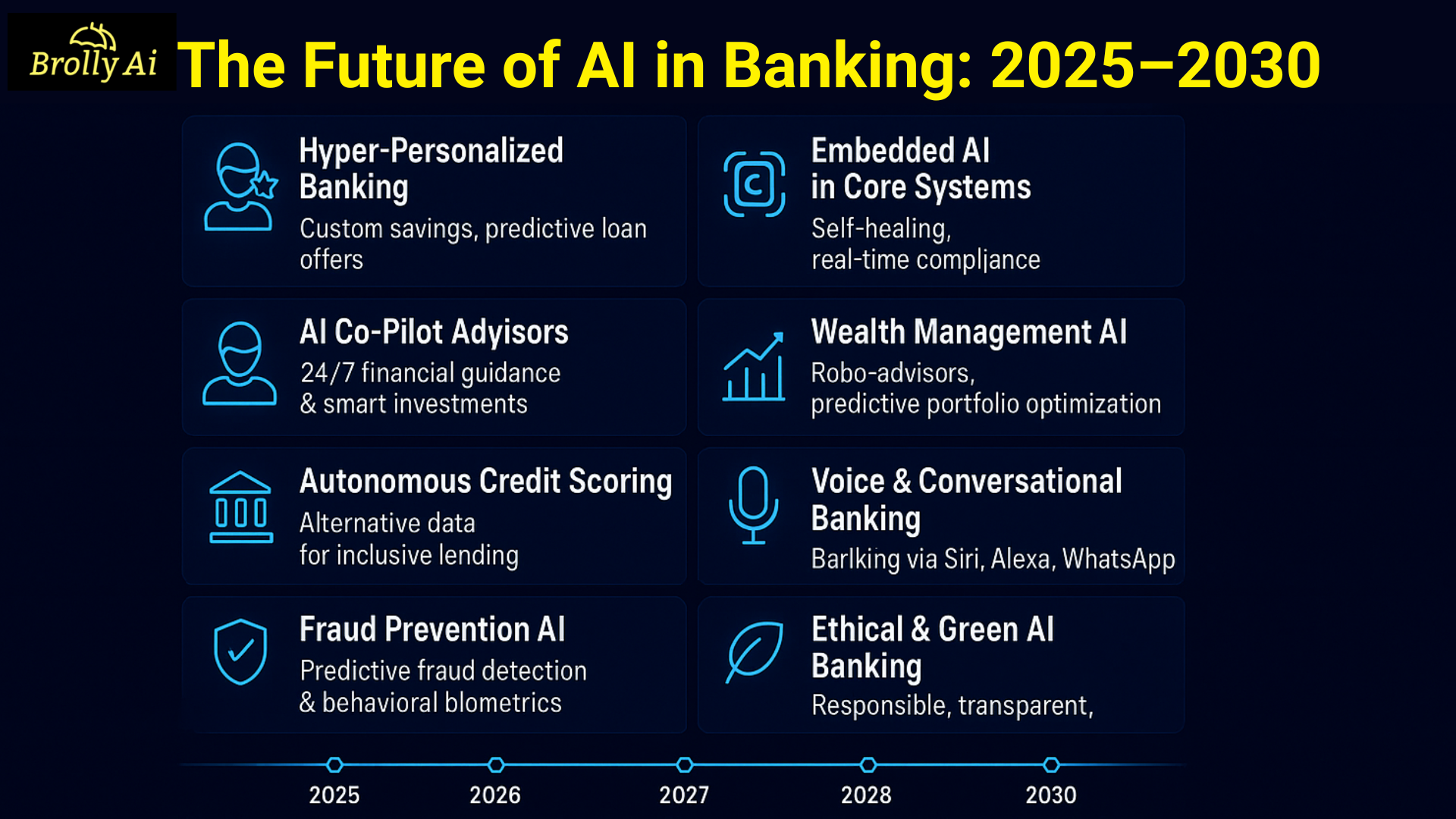
1. Hyper-Personalized Banking Experiences
Banks will move beyond generic recommendations to deep personalization based on:
- Real-time behavior tracking
- Life stage, income level, and spending patterns
- Emotional sentiment (using NLP and AI voice analysis)
Future example: Your banking app might suggest custom savings plans right after you receive your salary or notify you of better loan options when you begin house hunting — all based on intelligent prediction.
2. AI Co-Pilots and Financial Advisors
AI will act as a 24/7 financial advisor, helping customers manage money smarter with:
- Spending insights and budgeting tips
- Smart goal-based investment advice
- Real-time alerts for risky transactions
Voice-enabled AI assistants like JARVIS in banking may become a reality — available through WhatsApp, Alexa, or bank apps.
3. Global Expansion of AI-Driven Neo Banks
AI is the backbone of digital-only banks (neo banks) that have no physical branches but offer full banking services through apps.
Features include:
- Instant KYC using face recognition
- AI-powered credit scoring
- 24/7 chatbot support
- Instant loan disbursements
In India, players like Fi, Jupiter, NiyoX, and Zerodha-backed Neo Banks are leading the trend.
4. Autonomous Credit Scoring and Lending
Traditional credit scores will be replaced or enhanced by AI-powered creditworthiness assessments using:
- Payment behavior
- Mobile usage data
- Social signals (for micro-lending)
- Purchase trends
This will improve financial inclusion for people with limited banking history or no credit score — especially in rural India.
5. AI in Fraud Detection Will Evolve into Prevention
Today, AI helps detect fraud after it happens. In the future:
- AI will predict and prevent fraud in real time
- Behavioral biometrics will flag suspicious user behavior.
- AI-driven cybersecurity will become more predictive and adaptive.
Example: If someone logs into your account from an unfamiliar location at 3 AM and tries a large transfer, AI will block it instantly and alert you via call or WhatsApp.
6. Embedded AI in Core Banking Systems
Rather than AI being an external add-on, it will be embedded directly into the core systems:
- Autonomous risk models
- Real-time compliance flags
- Self-healing infrastructure (AI fixes issues automatically)
This will create self-optimizing banks that reduce manual intervention and human error.
7. Advanced AI Models for Wealth Management
For HNIs (High Net-Worth Individuals), banks will deploy:
- AI-powered Robo-advisors for portfolio optimization
- Predictive algorithms for equity, mutual funds, and crypto
- Real-time market monitoring and personalized updates
AI will make wealth management smarter and more accessible by using data-driven insights to serve a wider range of customers, not just the wealthy.
8. Conversational and Voice-Driven Banking
The rise of voice assistants like Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa will be integrated into banking:
- Check account balances
- Pay bills using voice.
- Book FDs or apply for loans via conversation
AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) will be key for banks to rank in voice search and assist customers effectively.
9. AI for Financial Literacy and Inclusion
Banks are set to roll out AI-powered financial education tools designed to suit different languages, learning levels, and customer needs.
- Regional languages
- Education levels
- Age and financial awareness
A rural customer in India might interact with an AI chatbot in Telugu or Hindi to learn how to open a savings account, apply for a loan, or understand UPI payments.
10. Sustainable and Ethical AI Banking
As AI becomes more deeply integrated into banking, the spotlight will shift toward responsible, ethical, and environmentally sustainable AI practices.
- Energy-efficient AI infrastructure
- AI models that promote ethical lending
- Transparent and inclusive algorithms
Many global banks have committed to green fintech goals, where AI plays a central role.
What the Future Holds: Key Predictions
Timeline | AI Milestone in Banking |
2025 | AI in 100% of customer interactions |
2026 | Real-time AI-based loan approvals |
2027 | Voice-based banking in 15+ Indian languages |
2028 | Fully AI-managed portfolios for all customer segments |
2030 | Autonomous banking with AI managing 80% of backend operations |
Final Thought
The future of AI in banking goes beyond automation — it’s focused on building intelligent, secure, and customer-first financial experiences. As the technology evolves, banks that embrace trustworthy, explainable, and inclusive AI will win the confidence of the next generation of global and Indian customers.
Real-World Case Studies of AI in Banking
Let’s explore how leading banks and financial institutions are already leveraging AI to revolutionize their operations and customer experiences. These real-life examples reveal how banks are using AI to drive innovation, deliver results, and transform the way financial services operate.
1. HDFC Bank – Eva (AI Chatbot)
Use Case: Customer Support
Technology: NLP-powered chatbot
HDFC Bank introduced Eva, a chatbot powered by Senseforth.ai, designed to handle customer queries through advanced AI.
- Answers more than 5 million queries per month
- Supports over 1,000 banking FAQs
- Available 24/7 on web and mobile platforms
Result: Improved customer support efficiency by 30% and reduced turnaround time.
2. ICICI Bank – iPal and Smart Lending
Use Case: Conversational banking + Loan processing
- iPal, the AI chatbot, handles 85% of customer queries automatically.
- ICICI Bank applies AI to evaluate credit risk and detect fraud during its loan approval process, ensuring faster and safer decisions.
Result: 50% faster loan processing and better fraud prevention.
3. JPMorgan Chase – COIN Platform
Use Case: Contract review automation
Technology: Machine Learning, NLP
COIN (Contract Intelligence) is an AI platform that:
- Analyzes legal documents
- Extracts critical data from 12,000+ contracts in seconds
- Reduces human error in legal processing
Result: Helped save over 360,000 hours annually in legal document review, boosting productivity and accuracy.
4. Bank of America – Erica
Use Case: Personal financial assistant
Technology: AI + Voice + NLP
Erica is an AI virtual assistant in the BoA mobile app. It helps users:
- Track expenses
- Pay bills
- Get FICO score updates.
- Set up savings goals.
Result: Over 25 million users have interacted with Erica, completing 100+ million client requests.
5. SBI – YONO and AI-Driven Risk Management
Use Case: Digital banking & credit risk management
- YONO app uses AI for personalized product offers and fraud detection.
- SBI applies AI in risk scoring, especially for SME and retail lending.
Result: Enhanced loan quality and deeper financial inclusion.
6. DBS Bank – AI for Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
Use Case: Compliance and fraud detection
Technology: AI + Deep Learning
DBS uses AI to:
- Monitor unusual transaction patterns
- Detect possible money laundering activities.
- Automate suspicious activity reports (SAR)
Result: Boosted compliance accuracy and reduced false positives by 35%.
7. Wells Fargo – Predictive Banking
Use Case: Personalized customer alerts
Wells Fargo built a predictive AI engine that sends:
- Bill reminders
- Budget alerts
- Unusual spending notifications
Result: Increased app usage and encouraged users to manage their finances more effectively.
8. Axis Bank – AI in Fraud Detection
Use Case: Real-time fraud monitoring
Axis Bank implemented an AI model that:
- Detects unusual ATM or debit card transactions
- Blocks suspicious activity instantly
- Notifies customers via SMS/app push
Result: Fraud losses reduced significantly and customer trust improved.
9. HSBC – AI for Transaction Monitoring
Use Case: AML and KYC compliance
HSBC collaborated with AI firms like Ayasdi to build machine learning tools that:
- Detect hidden patterns in millions of transactions
- Identify complex money laundering behavior.
- Automate risk flagging and compliance alerts
Result: Increased regulatory efficiency and reduced manual effort.
10. Goldman Sachs – AI in Investment Banking
Use Case: Market forecasting and trading
Goldman Sachs uses:
- AI models for stock prediction
- Machine learning for trade execution
- NLP to analyze news sentiment and market events
Result: Faster decision-making and smarter trading strategies.
Final Summary
These case studies clearly demonstrate that AI in banking is not futuristic — it’s already here, driving measurable results. From chatbots to fraud detection, credit risk to customer experience, the top banks across India and the globe are using AI to:
- Cut costs
- Boost customer engagement
- Drive financial innovation
- Strengthen compliance and safety.
Conclusion
The application of AI in banking is no longer a futuristic vision—it’s a powerful present-day reality. From fraud detection to personalized customer experiences, AI is reshaping the financial industry in ways we couldn’t imagine a decade ago. Whether it’s chatbots answering millions of queries or machine learning models detecting complex money-laundering patterns, AI is driving efficiency, innovation, and inclusion across banking operations.
Banks in India and around the world are leveraging AI not just for profitability, but also to build secure, accessible, and customer-friendly financial ecosystems. As this technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more intelligent, ethical, and inclusive banking experiences powered by AI.
- Embracing AI is not optional anymore—it’s essential for banks to stay relevant and competitive in a digital-first world.
FAQs
AI in banking refers to using technologies like machine learning, chatbots, and data analytics to automate, optimize, and personalize banking operations. It improves customer service, fraud detection, credit scoring, and more.
AI detects fraudulent transactions by identifying unusual patterns and anomalies in real-time. It uses historical data and predictive algorithms to reduce fraud risks and alert authorities instantly.
AI automates repetitive tasks, but it won’t fully replace human employees. Instead, it enhances productivity, allowing staff to focus on complex and relationship-driven tasks.
AI chatbots are virtual assistants that use natural language processing (NLP) to interact with customers. They handle queries, help with transactions, and are available 24/7.
Yes, when implemented securely, AI enhances safety by strengthening cybersecurity, monitoring risks, and preventing fraud through real-time detection systems.
AI in India is improving digital banking, credit risk scoring for rural borrowers, and automating services through tools like HDFC’s Eva and SBI’s YONO.
Leading banks like HDFC, ICICI, SBI, Axis Bank, and Kotak Mahindra are actively using AI for chatbots, fraud detection, credit underwriting, and customer service.
AI assesses a borrower’s creditworthiness using alternative data like transaction history, spending habits, and behavioral patterns, providing faster and fairer credit scores.
It means using AI to deliver personalized product recommendations, financial advice, or loan offers based on each customer’s preferences and behaviors.
Yes. AI enables banks to serve underbanked populations by analyzing alternative credit data and automating onboarding processes, especially in rural areas.
Absolutely. AI speeds up loan approvals by analyzing customer data quickly, verifying documents, predicting risk, and ensuring compliance with lending policies.
Challenges include data privacy concerns, bias in algorithms, regulatory compliance, and high implementation costs for smaller banks.
AI-powered virtual assistants can resolve FAQs, guide users through transactions, and escalate complex issues to human agents when needed.
The future involves hyper-personalized banking, smarter fraud prevention, autonomous financial planning, and better regulatory compliance through AI.
Yes, AI can flag suspicious activities and transactions that may indicate money laundering by analyzing large data sets and behavioral patterns.
In investment banking, AI is used for algorithmic trading, market prediction, portfolio optimization, and analyzing financial news in real-time.
Machine learning enables banks to build predictive models for fraud detection, loan approvals, customer segmentation, and churn prediction.
Yes. AI helps banks stay compliant by automating reporting, detecting anomalies, and monitoring transactions for regulatory violations.
Banks use historical and real-time data to train AI models. They collaborate with data scientists and fintech companies to build customized solutions.
Risks include model inaccuracies, lack of transparency, data misuse, and reliance on biased datasets. Proper governance is essential.
Generative AI creates new content like reports, chat conversations, or investment suggestions. It’s being explored for content automation and advisory services.
Yes. AI automates KYC (Know Your Customer), identity verification, and document analysis, making onboarding faster and error-free.
XAI ensures that AI decisions are transparent and understandable to humans, especially in areas like credit approvals or fraud detection.
AI in apps powers virtual assistants, spending analysis, smart alerts, and personalized offers based on user behavior and preferences.
Automation follows predefined rules (like RPA), while AI learns and adapts using data, making decisions without being explicitly programmed.
Yes, thanks to cloud-based AI tools and fintech partnerships, even small or regional banks can adopt affordable AI solutions.
Not at all. AI benefits banks of all sizes by improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing customer experience.
Customers benefit from faster service, better loan access, fraud protection, and personalized experiences through AI-enabled systems.
Examples include HDFC’s Eva chatbot, BoA’s Erica assistant, JPMorgan’s COIN platform, and SBI’s YONO app—each using AI for practical tasks.
Not entirely. AI will reduce dependency on branches, but physical locations will continue to serve for complex needs and relationship banking.
