Characteristics of AI Systems
Introduction to AI Systems
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems are designed to learn from data
Unlike traditional software that follows fixed rules, AI systems analyze data patterns and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for every situation. - AI systems can adapt to changing inputs and environments
As new data becomes available, AI systems adjust their behavior, making them suitable for real-world scenarios where conditions are constantly changing. - AI systems support intelligent decision-making
By processing large volumes of data, AI systems can generate insights, predictions, or recommendations that help humans make faster and more accurate decisions. - Understanding AI characteristics makes AI easier to learn
When students and beginners know how AI systems learn, adapt, and decide, complex AI concepts become simpler and less intimidating. - AI characteristics are directly linked to career skills
Professionals and job seekers can better identify which AI skills are relevant for roles in data science, machine learning, automation, and analytics. - Businesses use AI characteristics to solve real problems
Organizations rely on AI’s learning, automation, and data-handling abilities to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and scale operations. - This guide explains what makes AI different from traditional software
It breaks down the core features that separate AI systems from rule-based programs, using clear explanations and real-world examples.
What Are Artificial Intelligence (AI) Systems?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems are computer-based systems that can learn from data and perform tasks that normally require human intelligence.
These tasks include recognizing patterns, understanding language, making predictions, and supporting decisions. - AI systems do not rely only on fixed rules.
Instead of being programmed step by step, they use data to understand how things work and improve their performance over time. - AI systems are designed to handle complexity and uncertainty.
They can work with large amounts of data, identify trends, and respond to situations where exact instructions are not available.
How Do AI Systems Work?
- Data Collection
AI systems start with data such as text, images, videos, numbers, or sensor information collected from real-world sources. - Learning from Data
The system analyzes this data to identify patterns, relationships, and trends using learning models. - Model Training and Improvement
AI systems continuously improve by adjusting themselves based on feedback and new data. - Decision-Making or Prediction
Based on what they have learned, AI systems make decisions, predictions, or recommendations. - Human Oversight
In most real-world applications, humans review, guide, or control AI-generated outcomes.
How Are AI Systems Different from Traditional Software?
The key difference between AI systems and traditional software lies in how they work, learn, and make decisions. Traditional software follows fixed instructions, while AI systems learn from data and improve over time.
AI Systems vs Traditional Software
Aspect | Traditional Software | Artificial Intelligence (AI) Systems |
Core Approach | Follows predefined rules written by developers | Learns patterns from data |
Learning Ability | Cannot learn or improve on its own | Continuously learns from new data |
Adaptability | Remains static unless manually updated | Adapts to changing inputs and environments |
Decision-Making | Produces fixed outputs for given inputs | Makes data-driven predictions and decisions |
Handling Complexity | Struggles with large or unstructured data | Efficiently handles large, complex datasets |
Scalability | Limited scalability | Highly scalable with more data |
Error Handling | Requires manual debugging | Improves accuracy through feedback |
Real-World Examples | Calculator, billing software, rule-based forms | Recommendation systems, fraud detection, chatbots |
Why This Difference Matters
- AI systems are better suited for real-world problems where conditions keep changing.
- Traditional software works well for fixed, predictable tasks.
- Understanding this difference helps learners and businesses choose the right technology for their needs.

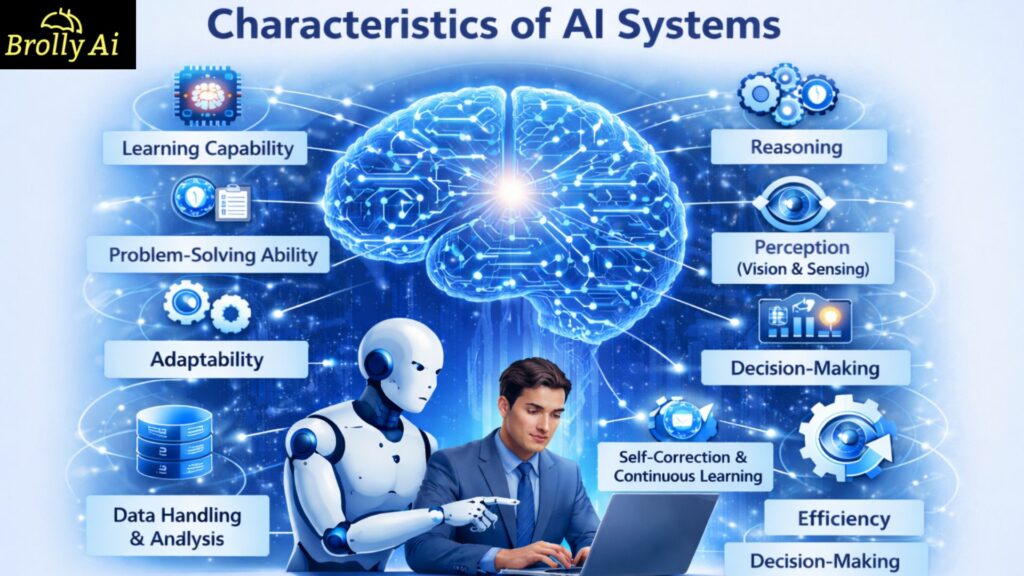
Top 11 Characteristics of AI Systems
1. Learning Capability
Learning capability is the most important characteristic of AI systems. It allows AI to improve performance by learning from data instead of relying on fixed rules.
How Do AI Systems Learn from Data?
AI systems learn by analyzing data and identifying patterns. This learning happens through different approaches, depending on the type of problem.
- Supervised Learning
The AI is trained using labeled data, where the correct output is already known.
Example: Email spam detection, image classification. - Unsupervised Learning
The AI learns from unlabeled data by discovering hidden patterns or groupings.
Example: Customer segmentation, anomaly detection. - Reinforcement Learning
The AI learns by interacting with an environment and improving its actions through rewards and penalties.
Example: Game-playing AI, robotics, autonomous systems.
Example of Learning in AI Applications
- Recommendation Engines
AI systems learn from user behavior such as clicks, searches, and watch history to suggest relevant products or content. - Fraud Detection Systems
AI analyzes transaction patterns and continuously learns to identify suspicious or abnormal activities in real time.
2. Problem-Solving Ability
Problem-solving ability allows AI systems to analyze complex situations, evaluate multiple possibilities, and identify the most effective solution using data-driven approaches.
How AI Solves Complex Problems
AI systems solve problems by processing large amounts of data and applying intelligent techniques such as:
- Optimization
AI evaluates many possible solutions and selects the one that delivers the best outcome based on defined goals and constraints. - Prediction
AI uses historical data to forecast future outcomes, helping in planning and decision-making. - Pattern Discovery
AI identifies hidden relationships and trends in data that are difficult for humans to detect manually.
Example of AI in Problem-Solving
- Route Optimization
AI systems analyze traffic conditions, distance, and time constraints to determine the most efficient routes in real time. - Medical Diagnosis
AI examines medical images, patient history, and clinical data to assist doctors in identifying diseases more accurately and quickly.
3. Reasoning
Reasoning enables AI systems to draw conclusions, make inferences, and solve problems logically based on available information. It helps AI move beyond data analysis to intelligent decision support.
What Is Logical Reasoning in AI?
AI systems use reasoning to evaluate facts, rules, and probabilities in order to reach conclusions. The two common forms of reasoning are:
- Rule-Based Reasoning
AI follows predefined logical rules to make decisions.
Example: If–then rules used in expert systems. - Probabilistic Reasoning
AI makes decisions based on likelihoods and uncertainty, especially when complete information is not available.
Example: Risk assessment models and predictive systems.
Real-World Applications of AI Reasoning
- Risk Analysis
AI evaluates multiple risk factors to estimate potential outcomes in areas such as finance, insurance, and cybersecurity. - Expert Systems
AI systems replicate human expert decision-making by applying reasoning rules in domains like medical diagnosis and technical troubleshooting.
4. Perception
Perception allows AI systems to understand and interpret information from the physical world using visual, audio, and sensory data. This capability helps AI “see,” “hear,” and respond to real-world inputs.
How AI Interprets Visual and Sensory Data
AI systems process different types of sensory data to understand their surroundings:
- Image Understanding
AI analyzes images to identify objects, patterns, and visual features. - Video Understanding
AI processes sequences of images to recognize actions, movements, and events over time. - Audio Understanding
AI interprets sound signals such as speech, music, or environmental noise.
Computer Vision as a Form of AI Perception
Computer vision enables AI systems to extract meaningful information from visual data.
- Face Recognition
AI systems identify and verify individuals by analyzing facial features. - Medical Imaging
AI assists healthcare professionals by detecting abnormalities in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with high accuracy.
5. Adaptability
Adaptability enables AI systems to adjust their behavior when new data, patterns, or conditions appear. This makes AI systems suitable for real-world environments where change is constant.
Why AI Systems Are Dynamic
AI systems are not static programs. They evolve over time because:
- Models update with new data
AI systems continuously learn from fresh data, improving accuracy and relevance without rewriting the entire system. - Changing environments are handled automatically
AI adapts to new user behavior, market trends, or external conditions. - Performance improves over time
As more data becomes available, AI systems become smarter and more reliable.
Example of AI Adaptability in Real Time
- Cybersecurity Threat Detection
AI systems monitor network activity and adapt instantly to new attack patterns, helping detect unknown or emerging cyber threats faster than traditional rule-based security tools.
6. Automation
Automation is a key characteristic of AI systems that enables tasks to be performed automatically with minimal human involvement. This helps organizations save time, reduce errors, and improve efficiency.
How AI Automates Repetitive Tasks
AI systems automate tasks by learning patterns and executing actions consistently across processes:
- Workflow Automation
AI manages end-to-end workflows such as data entry, report generation, and approval processes. - Process Automation
AI handles repetitive and rule-based tasks at scale, reducing manual effort and operational delays. - Error Reduction
Automated AI systems minimize human mistakes by following optimized decision paths.
Role of AI in Industrial and Business Automation
- Manufacturing
AI automates quality inspection, predictive maintenance, and production scheduling to improve output and reduce downtime. - Customer Support
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants handle common queries, provide instant responses, and escalate complex issues to human agents when needed.
7. Data Handling Capability
Data handling capability allows AI systems to collect, process, and analyze massive volumes of data efficiently. This is essential because modern AI systems depend on data to learn, adapt, and make accurate decisions.
How AI Manages Large Data Sets
AI systems are designed to work with different types of data at scale:
- Structured Data
Organized data such as databases, spreadsheets, and transaction records that follow a predefined format. - Unstructured Data
Raw data such as text, images, videos, audio, emails, and social media content that do not follow a fixed structure. - High-Speed Processing
AI systems can process data in real time or near real time, even when dealing with millions of records.
Example of AI in Big Data Processing
- Predictive Analytics
AI analyzes historical and real-time data to predict future trends, customer behavior, demand patterns, and potential risks, helping organizations make proactive decisions.
8. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables AI systems to understand, interpret, and respond to human language in a meaningful way. This allows humans to interact with AI using natural speech or text instead of technical commands.
How AI Understands Human Language
AI systems analyze language using multiple techniques to extract meaning and intent:
- Text Analysis
AI processes written language to understand grammar, keywords, and context. - Speech Recognition
AI converts spoken language into text and understands voice commands. - Sentiment Analysis
AI identifies emotions or opinions expressed in text or speech, such as positive, negative, or neutral sentiment.
Everyday Applications of NLP
- Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots answer user questions, provide support, and guide customers in real time. - Voice Assistants
AI systems understand spoken commands to perform tasks such as setting reminders, searching information, or controlling smart devices.
9. Self-Correction and Continuous Learning
Self-correction and continuous learning allow AI systems to improve their performance over time by learning from mistakes, feedback, and new data. This makes AI systems more accurate, reliable, and effective as they are used.
How AI Improves Accuracy Over Time
AI systems refine their performance through ongoing learning processes:
- Feedback Loops
AI systems receive feedback from users or outcomes, helping them understand where predictions or decisions were incorrect. - Model Retraining
AI models are periodically retrained with updated data so they can adjust to new patterns and reduce errors. - Performance Optimization
Continuous evaluation helps AI systems improve speed, accuracy, and decision quality over time.
Example of Self-Correcting AI Systems
- Speech Recognition Systems
AI-powered speech systems improve voice recognition accuracy by learning from different accents, pronunciations, and speaking styles as more users interact with them.
10. Efficiency
Efficiency is a core characteristic of AI systems that enables faster processing, higher accuracy, and consistent performance across large-scale operations.
How AI Improves Speed and Accuracy
AI systems are designed to handle tasks quickly and precisely:
- Faster Processing
AI can analyze large volumes of data in seconds, a task that would take humans hours or days. - Fewer Errors
By reducing manual intervention, AI systems minimize human errors and deliver consistent results. - Continuous Performance
AI systems operate 24/7 without fatigue, ensuring uninterrupted productivity.
AI’s Role in Business Productivity
- Cost Reduction
AI automates repetitive tasks and optimizes resource usage, lowering operational costs. - Scalability
AI systems can easily scale to handle increased workloads without significant additional resources.
11. Decision-Making
Decision-making enables AI systems to analyze data, evaluate possible outcomes, and support or make informed decisions. This characteristic allows AI to assist humans in complex and high-volume decision scenarios.
How AI Makes Decisions
AI systems rely on data-driven models to evaluate options and predict outcomes:
- Probabilistic Models
AI estimates the likelihood of different outcomes when uncertainty is involved, helping in risk-based decisions. - Predictive Models
AI uses historical and real-time data to forecast future results and recommend the best possible actions. - Decision Support, Not Replacement
In most applications, AI supports human decision-making rather than fully replacing it.
AI-Assisted Decision-Making in Real Life
- Credit Scoring
AI evaluates financial data, spending patterns, and risk factors to help financial institutions assess creditworthiness. - Hiring Tools
AI assists recruiters by screening resumes, matching skills, and predicting candidate suitability while final decisions remain with humans.

Characteristics of AI Systems in Practice
This section shows how the characteristics of AI systems—such as learning, adaptability, automation, and decision-making—are applied in real-world industries to solve practical problems.
Applications of AI Across Industries
Healthcare
- Diagnosis: AI analyzes medical images, reports, and patient data to assist doctors in detecting diseases earlier and more accurately.
- Drug Discovery: AI accelerates research by identifying potential drug compounds and predicting their effectiveness.
Finance
- Fraud Detection: AI monitors transactions in real time to identify suspicious patterns and prevent financial fraud.
- Trading: AI-powered systems analyze market trends and execute data-driven trading strategies.
Marketing
- Personalization: AI tailors content, product recommendations, and offers based on user behavior and preferences.
- Ad Targeting: AI optimizes ad delivery by identifying the right audience at the right time.
Education
- Adaptive Learning: AI customizes learning paths based on individual student performance, pace, and learning style.
Manufacturing
- Predictive Maintenance: AI analyzes equipment data and usage patterns to identify potential failures in advance, allowing maintenance to be performed proactively, minimizing downtime and reducing overall maintenance costs.
Human–Machine Interaction
Human–machine interaction focuses on how people and AI systems work together to achieve better outcomes. Instead of replacing humans, AI is designed to support, assist, and enhance human capabilities.
Collaboration Between Humans and AI
- AI handles data-intensive tasks
AI processes large volumes of data, identifies patterns, and provides insights that would be difficult or time-consuming for humans to analyze manually. - Humans provide context and judgment
People use experience, ethics, and critical thinking to interpret AI outputs and make final decisions. - Shared decision-making
AI supports humans with recommendations, while humans retain control over important actions and outcomes.
Why AI Augments, Not Replaces, Human Intelligence
- AI lacks human creativity and emotional intelligence
AI operates on data and algorithms, while humans bring intuition, empathy, and creativity. - AI depends on human guidance
Humans design, train, monitor, and correct AI systems to ensure responsible and accurate performance. - Best results come from collaboration
Combining human expertise with AI’s speed and accuracy leads to more effective and reliable outcomes.
Ethical Considerations in AI Systems
Ethical considerations ensure that AI systems are developed and used responsibly, safely, and fairly. As AI becomes more integrated into daily life and business decisions, addressing ethical issues is critical.
Bias and Fairness
- Bias in data can lead to biased AI outcomes
If training data reflects human bias or imbalance, AI systems may produce unfair or discriminatory results. - Fairness requires diverse and representative data
AI systems must be trained on balanced datasets to ensure equal treatment across different groups. - Continuous monitoring is essential
Regular evaluation helps detect and correct bias as AI systems evolve.
Transparency and Explainability
- Users should understand how AI makes decisions
Transparent AI systems explain the factors influencing their outputs. - Explainability builds trust
When users can interpret AI decisions, confidence and acceptance increase. - Regulatory and business importance
Many industries require explainable AI to meet compliance and accountability standards.
Responsible AI Usage
- Human oversight must be maintained
AI systems should support human decisions, not operate without supervision in critical areas. - Ethical guidelines and governance
Organizations must follow ethical frameworks to ensure safe and responsible AI deployment. - Long-term impact awareness
Responsible AI considers social, legal, and environmental effects alongside technical performance.
Future Trends in AI Systems
AI systems are evolving rapidly, with future developments focused on greater autonomy, intelligence, and responsible use. These trends will shape how AI is built, governed, and applied across industries.
Autonomous AI Systems
- Greater independence in task execution
Future AI systems will handle complex workflows with minimal human intervention while still operating within defined boundaries. - Real-time learning and adaptation
Autonomous AI will continuously learn from live data, allowing faster responses to changing environments. - Expanded use cases
Applications include robotics, smart infrastructure, and advanced decision-support systems.
Smarter Decision Engines
- Improved predictive accuracy
AI decision engines will use advanced models to deliver more reliable and context-aware recommendations. - Multi-source data integration
Future systems will combine data from multiple sources to enhance decision quality. - Human-centered decision support
AI will increasingly focus on assisting humans rather than making fully independent decisions.
Stronger AI Regulations and Ethics
- Clear regulatory frameworks
Governments and organizations will implement stricter rules to govern AI development and deployment. - Focus on transparency and accountability
Ethical standards will require AI systems to be explainable and auditable. - Responsible AI adoption
Ethical considerations will become a core part of AI system design and business strategy.
Conclusion
The characteristics of AI systems define how intelligent, scalable, and useful these systems are in real-world applications. Features such as learning capability, adaptability, automation, and decision-making enable AI to solve complex problems more efficiently than traditional software.
Understanding these fundamentals is essential for anyone looking to build a career in AI, adopt AI solutions in business, or make informed decisions about technology. A clear grasp of how AI systems work helps individuals and organizations use AI responsibly, effectively, and with confidence in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.

FAQs
AI systems are characterized by learning capability, adaptability, automation, data handling, reasoning, perception, efficiency, and decision-making.
Learning capability allows AI systems to improve performance over time by learning from data instead of relying on fixed rules.
AI systems learn from data and adapt over time, while traditional software follows predefined rules and requires manual updates.
AI systems can make data-driven recommendations or decisions, but human oversight is usually required in critical applications.
Yes, many AI systems improve continuously through feedback, retraining, and exposure to new data.
AI systems use structured data (databases, spreadsheets) and unstructured data (text, images, audio, video).
Adaptability refers to an AI system’s ability to adjust its behavior based on new data or changing conditions.
AI uses advanced algorithms and computing power to process and analyze large volumes of data efficiently.
Automation in AI means performing repetitive or complex tasks automatically with minimal human involvement.
AI improves efficiency by processing data faster, reducing errors, and operating continuously without fatigue.
Reasoning allows AI to draw conclusions and make logical inferences using rules or probabilities.
Perception enables AI to interpret images, videos, audio, and sensory data from the real world.
NLP allows AI systems to understand, interpret, and respond to human language in text or speech form.
AI systems use feedback loops and retraining to identify errors and improve accuracy over time.
Decision-making in AI involves analyzing data and predicting outcomes to support or recommend actions.
AI systems are designed to support and augment human work, not fully replace human intelligence.
AI systems assist in diagnosis, medical imaging, drug discovery, and personalized treatment planning.
AI helps businesses improve productivity, reduce costs, automate processes, and make data-driven decisions.
AI detects unusual patterns, adapts to new threats, and helps prevent cyberattacks in real time.
Predictive analytics uses AI to analyze historical data and forecast future outcomes or trends.
AI accuracy depends on data quality, model design, and continuous monitoring.
Human–machine interaction refers to collaboration where AI supports human decision-making and tasks.
Key concerns include bias, fairness, transparency, accountability, and responsible usage.
Bias often comes from unbalanced or biased training data and improper model design.
Transparency helps users understand how AI makes decisions, building trust and accountability.
Healthcare, finance, marketing, education, manufacturing, and cybersecurity heavily use AI systems.
Autonomous AI systems can perform tasks independently while operating within defined boundaries.
Future AI systems will be more autonomous, ethical, explainable, and human-centered.
No, understanding basic AI characteristics makes learning AI concepts easier and more approachable.No, understanding basic AI characteristics makes learning AI concepts easier and more approachable.
AI fundamentals help individuals stay relevant in the job market and make informed technology decisions.
