MLOps Roadmap (2025): How Do You Become an MLOps Engineer From Scratch?

What Is MLOps and Why Does It Matter in 2025?
What Is MLOps in Simple Terms?
MLOps — short for Machine Learning Operations — is the discipline of taking machine learning models out of notebooks and putting them into the real world.
In simple words
MLOps is everything that happens after you train a machine learning model — deploying it, monitoring it, improving it, and keeping it reliable.
It connects three major skill areas
- Machine Learning — building and training models
- DevOps — automating delivery, testing, and infrastructure
- Data Engineering — managing data pipelines and versioning
Together, these create a smooth, repeatable, automated ML workflow.
Why Does MLOps Matter More Than Ever in 2025?
In 2025, companies are deploying not just ML models, but LLMs, agentic AI systems, and RAG pipelines.
This means ML systems are becoming
- More complex
- More data-dependent
- More dynamic
- More expensive to maintain
- More business-critical
Without solid MLOps, these systems fail quickly.
The real challenge in 2025 is not building AI — but running it.
Some reasons why MLOps is booming:
AI adoption is increasing across every industry
Finance, healthcare, e-commerce, startups — everyone wants automated ML pipelines.
LLMOps and RAG systems introduce new operational demands
You need monitoring for
- hallucinations
- context quality
- prompt drift
- vector store performance
Traditional ML workflows are not enough.
Companies need reproducible, stable, cost-efficient ML systems
AI can become expensive without version control, CI/CD, or automated retraining.
Regulatory pressure is increasing
Governments and enterprises expect
- explainability
- fairness
- audit trails
- compliance
MLOps supports all of these.
How Does MLOps Work in Real Life?
Here’s a simple example:
A retail company trains a fraud detection model.
Initially, it works well — but after 3 months, fraud patterns change.
Without MLOps:
Model accuracy drops
Customers get false alerts
Revenue declines
Retraining takes weeks
No one knows why the model drifted
With MLOps:
Data is versioned
Drift is detected in real time
Retraining happens automatically
Models deploy via CI/CD
Monitoring alerts for engineers
This shift — from “build once” to “continuous improvement” — is the heart of MLOps.
Where Does MLOps Fit in the AI/ML Landscape in 2025?
MLOps sits at the centre of modern AI development.
MLOps now powers
- Machine learning pipelines
- Deep learning models
- NLP systems
- LLM-based applications
- Multi-agent workflows
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems
- Vector database pipelines
- Autonomous AI agents
The industry calls this expanded domain
LLMOps + MLOps: The foundation of scalable AI in 2025.
The Bottom Line
If you want to build a career in AI — whether you’re a beginner or a professional — you must understand MLOps.
It is one of the most in-demand, highest-paying, and fastest-growing skills today.
What Are the Key Components of a Modern MLOps Pipeline?
A modern MLOps pipeline is more than “train a model and deploy.”
It’s a system — a series of coordinated steps that take ML from experimentation to reliable production.
Let’s break it down in a simple, clear, practical way.
How Does Data Flow Through an MLOps System? (High-Level Overview)
A complete MLOps workflow usually follows this path
- Data ingestion
- Data versioning + validation
- Feature engineering & feature storage
- Model training & experiment tracking
- Model packaging (Docker, containers)
- Deployment (API, batch, streaming, or serverless)
- Monitoring & logging
- Drift detection
- Automated retraining pipelines
In 2025, this process also includes handling
- LLMs
- RAG pipelines
- Vector databases
- AI agents
- Governance & compliance
Because modern AI products are not static — they evolve constantly.
What Are the Critical Components You Must Understand?
Below is a breakdown of each key MLOps component + why it matters.
1. Data Versioning: How do you track changes in ML datasets?
Data is the “code” of ML.
If data changes, your model changes.
Tools like DVC, LakeFS, and Git LFS help you
- Track datasets
- Reproduce experiments
- Manage large files
- Roll back versions
Why it matters
It prevents “Model worked yesterday but not today” problems.
2. Feature Engineering & Feature Stores
You need clean, consistent features across training, testing, and production.
Feature stores help
- Store reusable features
- Ensure consistent transformations
- Reduce data leakage
Popular tools: Feast, Hopsworks
3. Model Training & Experiment Tracking
Experimentation gets chaotic fast.
Tools like MLflow, Weights & Biases, and Neptune help track
- Hyperparameters
- Metrics
- Artifacts
- Training logs
Why it matters
You can compare experiments, replicate results, and pick the best model.
4. Model Packaging (Containerization)
To deploy ML models anywhere, package them in a predictable environment.
Tools used
- Docker
- Conda environments
- Poetry
Why it matters
No more “It works on my machine.”
5. Model Deployment
There are four main deployment methods
- Real-time API deployment (FastAPI, Flask)
- Batch inference (scheduled jobs)
- Streaming inference (Kafka, Flink)
- Serverless ML (AWS Lambda, Cloud Run)
2025 trend:
LLMs deployed via
- LangServe
- BentoML
- Kubernetes-based inference servers
6. Monitoring & Logging
Monitoring ensures your model behaves as expected.
You track
- Latency
- Accuracy
- Input anomalies
- Cost
- Hardware usage
- LLM hallucinations (new in 2025)
- Vector database recall in RAG systems
Tools include: Prometheus, Grafana, WhyLabs, EvidentlyAI
7. Drift Detection (Data + Concept Drift)
Drift means your model has moved away from reality.
Two types
- Data Drift: input data changes
- Concept Drift: labels or relationships change
Modern pipelines use drift detectors to trigger alerts or retraining.
8. Automated Retraining Pipelines
Retraining happens automatically when
- Drift is detected
- New data arrives
- Performance drops
Orchestrated by
- Kubeflow Pipelines
- Airflow
- Prefect
This ensures ML stays fresh and reliable.
Table: Components of MLOps Pipeline (With Tools)
Component | Purpose | Popular Tools (2025) |
Data Versioning | Track dataset changes | DVC, LakeFS, Git LFS |
Feature Engineering | Consistent data transformations | Feast, Hopsworks |
Training & Tracking | Track experiments | MLflow, W&B |
Packaging | Reproducible environments | Docker, Conda |
Deployment | Serve models | FastAPI, BentoML, Kubernetes |
Monitoring | Track performance | Prometheus, Grafana, EvidentlyAI |
Drift Detection | Alerts on data/model changes | WhyLabs, EvidentlyAI |
Retraining Pipelines | Automated model updates | Kubeflow, Airflow |
Why Understanding These Components Is Non-Negotiable
Every MLOps job posting — from junior to senior — expects you to know:
How ML systems move from idea → deployment
What tools support each stage
How to troubleshoot failures
How to automate workflows
This section builds your foundation for the rest of the roadmap.
What Does the MLOps Lifecycle Look Like End-to-End?
The MLOps lifecycle is the backbone of everything you do as an MLOps engineer.
It describes how a model goes from an idea to a living, evolving, production-grade system.
Let’s break this down in a way that’s easy to understand — even if you’re just starting.
Why Is the MLOps Lifecycle Different From Traditional ML Development?
Traditional ML development is usually like this:
- Collect data
- Try different models in a notebook
- Get good accuracy
- Hand it off to someone else
- Hope it works
This approach works in college projects — but breaks instantly in real companies.
MLOps transforms ML from one-time experiments into repeatable, scalable processes.
In 2025, the lifecycle is more important than ever because models:
- interact with real-time data
- support real users
- integrate with APIs
- Use vector databases
- require continuous monitoring
- must follow governance and compliance
So instead of a one-way path, MLOps uses a continuous loop.
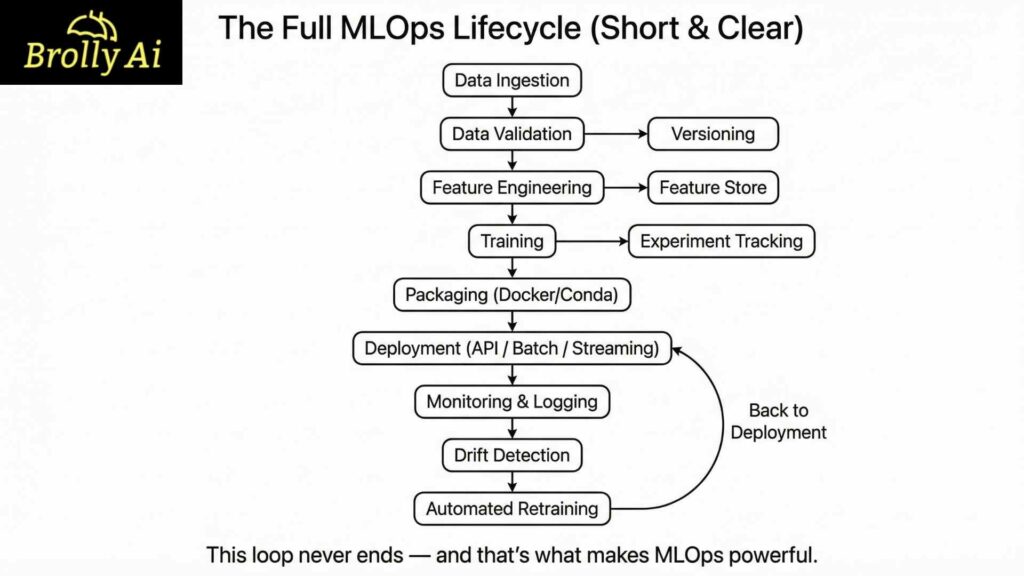
The MLOps Lifecycle (Simple, Real-World View)
Below are the major stages of a modern MLOps lifecycle.
1. Data Collection & Ingestion: Where does your data come from?
ML systems rely on diverse data sources such as:
- databases (SQL/NoSQL)
- APIs
- IoT streams
- logs
- third-party datasets
- real-time customer interactions
MLOps automates this data ingestion so models always see fresh, reliable data.
2. Data Validation & Versioning: How do you ensure data is correct?
Before training, data must be
- validated
- versioned
- checked for schema changes
- compared with previous versions
Tools like DVC, Great Expectations, and EvidentlyAI help ensure:
- no broken columns
- no missing features
- No faulty data injections
Reliable data = reliable ML.
3. Feature Engineering & Storage: How do you transform data?
This step includes
- cleaning
- encoding
- normalization
- feature extraction
In production, you must guarantee consistency:
The features you use in training must match the features generated in production.
Feature stores (Feast, Hopsworks) help centralise and reuse features across the organisation.
4. Model Training & Experiment Tracking: Which model performs best?
This is where the actual ML modelling happens — but with structure.
Instead of guessing, MLOps encourages
- tracking parameters
- logging metrics
- comparing results
- storing artifacts
Tools: MLflow, W&B, Neptune
This ensures every experiment is reproducible.
5. Model Packaging: How do you prepare a deployment model?
Models must run in predictable environments.
Packaging includes
- saving the model (pickle, ONNX, TorchScript)
- creating a Conda or Docker environment
- embedding inference code
This step avoids dependency conflicts and runtime errors.
6. Model Deployment: How does the model go live?
Deployment options
- Real-time API (FastAPI, Flask, BentoML)
- Batch jobs
- Streaming pipelines
- Serverless ML
- Kubernetes inference
In 2025, deployment must also support:
- LLMs
- RAG pipelines
- vector DB retrieval
- prompt templates
- agent frameworks
Deployment is no longer just “host an API” — it’s managing entire AI systems.
7. Monitoring & Logging: Is the model behaving correctly?
Once live, models must be monitored for
- accuracy or performance drop
- latency spikes
- rising inference costs
- data drift
- model drift
- hallucination rates (for LLMs)
- vector store recall (RAG-specific)
Monitoring tools help detect issues before they impact users.
8. Drift Detection: Has the world changed?
Drift happens when the environment changes.
Examples
- Fraud patterns change
- Customer behaviour shifts
- New product categories appear
- LLM answers become less accurate
Drift triggers alerts or automatic responses.
9. Automated Retraining: How do you keep the model updated?
Retraining pipelines
- pick up new data
- retrain the model
- re-validate performance
- Redeploy the updated version
- run automated tests
Orchestration tools: Kubeflow, Airflow, Prefect
This ensures your ML system stays fresh and competitive.
Text Diagram: The Full MLOps Lifecycle (Short & Clear)
Why This Lifecycle Matters for Your Career
Companies don’t hire people who can train models.
They hire people who can run ML in production.
Understanding this lifecycle:
helps you design real systems
improves your interviews
guides your learning path
Makes your resume stand out
prepares you for LLMOps challenges
This lifecycle is the core of every MLOps roadmap.

What Are the Essential Skills You Need to Start an MLOps Career?
Becoming an MLOps engineer doesn’t require you to be a math genius or a senior DevOps pro.
But you do need a balanced set of practical skills across coding, data, ML, and DevOps.
This section highlights only the skill areas that matter most, based on 2025 job descriptions and industry demand.
Why These Skills Matter
MLOps engineers work at the intersection of:
- ML (building the model)
- Engineering (running the model)
- Infrastructure (scaling the model)
That means your skillset must help you
- Build ML pipelines
- Deploy models
- Debug real systems
- Automate workflows
- Monitor production ML
Think of it like this:
ML teaches you what to build.
DevOps teaches you how to deliver it.
Data Engineering teaches you how to feed it.
MLOps teaches you how to run it all reliably.
Let’s break down exactly what you need.
1. Programming & Environment Skills: What Should You Learn First?
These are your foundation skills. Every MLOps engineer uses them daily.
Python (Non-negotiable)
Python is the main language for both ML and MLOps.
You should understand
- Functions, classes, modules
- Data structures
- Error handling
- Writing clean scripts
- Building small CLI tools
Why?
Because every model, pipeline, or deployment script starts with Python.
Bash & Linux Basics
Most ML workflows run in
- Linux servers
- Cloud environments
- Containers
- Remote VMs
So you must know how to
- Navigate directories
- Manage files
- Read logs
- Write shell scripts
- Automate tasks
Even simple Bash skills save hours.
Git & Version Control
Git is essential for
- Tracking code changes
- Collaborating with teams
- Managing your project structure
- Storing experiments and configs
In MLOps, GitOps is becoming the standard for deployment automation.
IDEs (VS Code, PyCharm)
You don’t need to master everything — just know how to:
- Manage environments
- Use extensions
- Debug code
- Work with Docker
- Connect to remote servers
2. Data Skills: How Important Is Data Engineering for MLOps?
Very important.
MLOps is more about data pipelines than machine learning models.
You should know
SQL
You must write SQL queries to:
- Extract datasets
- Clean data
- Prepare training sets
- Validate data quality
SQL is universal across companies.
Data Cleaning & Transformation
This includes
- Handling missing values
- Encoding categories
- Scaling numeric data
- Dealing with outliers
- Feature extraction
If your data is broken, your ML system will break with it.
Building Simple Data Pipelines
You don’t need to become a data engineer, but you should understand:
- batch vs real-time pipelines
- ETL basics
- cron jobs
- cloud storage (S3, GCS, Azure Blob)
Data pipelines are the fuel of every ML model.
3. ML Fundamentals: What Do You Actually Need to Know?
You don’t need deep math or PhD-level theory.
But you do need to understand the ML basics that matter in production.
Core ML Concepts
- Train/test/validation splits
- Overfitting & underfitting
- Hyperparameters
- Evaluation metrics
- Bias & fairness
This is the foundation of reliable ML.
ML Libraries You Must Know
At minimum
- Scikit-learn (classic ML)
- TensorFlow or PyTorch (deep learning)
- XGBoost or LightGBM (tabular data workhorses)
These will help you follow real ML workflows before adding MLOps layers on top.
4. DevOps & Infrastructure Skills: What Should You Learn for MLOps?
This is where MLOps becomes different from ML engineering.
Containers (Docker)
Docker allows you to
- package your model
- package dependencies
- guarantee reproducibility
- deploy anywhere
This is key for real-world ML deployment.
Kubernetes (Beginner to Intermediate)
You don’t need expert-level K8S skills, but you must understand:
- What pods are
- How deployments work
- basics of scaling
- using config maps & secrets
- working with inference workloads
In 2025, most AI systems run on Kubernetes or cloud-managed Kubernetes services.
CI/CD Concepts
MLOps depends on automation.
CI/CD does the heavy lifting
- test your code
- validate data
- build images
- deploy new models
You should understand tools like
- GitHub Actions
- GitLab CI
- Jenkins
You’ll use these to automate retraining and deployment pipelines.
Skill Summary Table (Beginner → MLOps-Ready)
Skill Area | What You Need to Know | Importance |
Python | Scripting, modules, automation | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Bash/Linux | Commands, SSH, logs | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Git | Branching, commits, PRs | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
SQL | Joins, filters, aggregations | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Data Cleaning | Feature engineering basics | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
ML Basics | Metrics, algorithms, tuning | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Docker | Build, run, images | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Kubernetes | Basic deployment concepts | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
CI/CD | Automated pipelines | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Why These Skills Together Matter
When combined, these skills let you
Build ML models
Package them reliably
Deploy them at scale
Monitor them in production
Automate updates and retraining
Work confidently in real teams
This is exactly what hiring managers look for in 2025.
What Tools Should You Learn in the MLOps Roadmap? (Focused 2025 Tools Landscape)
Learning MLOps tools can feel overwhelming, especially when you see giant diagrams with 100+ tools.
But here’s the truth:
You don’t need every tool.
You just need the right tools.
This section focuses only on the essential, industry-backed, and future-proof tools used in 2025.
Why Knowing the Tools Matters
Tools help you
- automate ML pipelines
- track experiments
- deploy models
- Monitor live systems
- manage data
- build reproducible environments
The goal isn’t to learn tools for the sake of learning, but to understand how they solve real MLOps problems.
Let’s explore the ones that matter most.
1. Tools for Data Versioning & Tracking
Data changes constantly.
Versioning ensures you can always reproduce results.
DVC (Data Version Control)
Best for: managing datasets + ML pipelines
Why it matters
- Works like Git for data
- Tracks experiments
- Integrates with cloud storage
- Lightweight and beginner-friendly
LakeFS
Best for: enterprise-level data versioning
Why it matters
- Git-like branching for large datasets
- Highly scalable for big organisations
Git LFS
Best for: storing large files
Useful for small/medium projects where heavy tooling isn’t needed.
2. Tools for Experiment Tracking
Tracking experiments ensures you know what worked — and what didn’t.
MLflow
Most widely used experiment tracker
Key features
- Tracks metrics
- Stores artifacts
- Provides a model registry
- Supports deployment
Perfect for both beginners and professionals.
Weights & Biases (W&B)
Best for deep learning + team collaboration
Why it’s popular
- Beautiful visual dashboards
- Hyperparameter sweeps
- Fast integration with PyTorch & TensorFlow
3. Tools for Pipeline Orchestration
These tools automate how your ML workflow runs in sequence.
Kubeflow Pipelines
Industry standard for ML pipelines on Kubernetes
Helps automate
- preprocessing
- training
- validation
- deployment
- retraining
Perfect for scalable projects.
Apache Airflow
Best for batch pipelines and ETL workflows
Used heavily in data engineering + ML teams.
Prefect
Simplest pipeline orchestration tool
Perfect for beginners building production-ready automation.
4. Tools for Model Deployment
You’ll deploy ML models as
- APIs
- batch jobs
- streaming services
- serverless functions
- LLM endpoints
These are the must-learn tools.
FastAPI
The fastest-growing ML deployment framework.
Why
- Easy to learn
- Async support
- High performance
- Great documentation
Docker
Not optional — a core MLOps skill.
Allows you to package ML models in reproducible environments.
GitHub Actions
The most common CI/CD tool for
- testing models
- validating data
- building Docker images
- deploying models
BentoML (2025 rising star)
Fantastic for LLM and ML model serving.
Supports
- GPU serving
- Model packaging
- LLM services
- Multi-model systems
5. Tools for Monitoring & Drift Detection
Monitoring is crucial because ML models degrade over time.
EvidentlyAI
Open-source monitoring tool.
Tracks
- data drift
- model drift
- performance metrics
WhyLabs
Enterprise-grade monitoring.
Great for large-scale ML deployments.
Prometheus + Grafana
Used for
- infrastructure logs
- latency monitoring
- API health monitoring
Essential skills for real-world ML systems.
6. Tools for LLMOps (2025 Must-Know Tools)
Modern MLOps now includes LLMOps — managing large language models.
Vector Databases (for RAG)
Must-learn tools
- Pinecone
- Weaviate
- FAISS
- ChromaDB
Without vector stores, RAG pipelines can’t function.
LangChain / LangGraph
Tools for building
- multi-step pipelines
- agent workflows
- LLM applications
Model Hosting Platforms
- HuggingFace Inference
- AWS Sagemaker
- GCP Vertex AI
Summary Table: MLOps Tools Landscape (2025)
Category | Tools to Learn | Why They Matter |
Data Versioning | DVC, LakeFS | Reproducibility & tracking |
Experiment Tracking | MLflow, W&B | Compare & manage experiments |
Pipelines | Kubeflow, Airflow, Prefect | Automate ML workflows |
Deployment | Docker, FastAPI, BentoML | Run models anywhere |
CI/CD | GitHub Actions | Automate testing & deployment |
Monitoring | EvidentlyAI, Prometheus | Detect drift & failures |
LLMOps | Pinecone, LangChain | Build LLM + RAG systems |
Why These Tools Matter More Than Others
The 2025 MLOps job market prioritises tools that:
support automation
integrate with cloud environments
are open source
work well with LLMs
scale easily
Learning these tools prepares you for real-world MLOps roles — not just theory.

How Do You Gain Practical MLOps Experience?
Learning MLOps theory is useful — but practical experience is what gets you hired.
Companies want engineers who can build, deploy, and maintain ML systems, not just explain concepts.
This section shows you exactly how to build hands-on experience—even if you are a beginner.
Why Practical Experience Matters More Than Courses
In 2025, MLOps roles require
- real project work
- real deployments
- real pipelines
- real monitoring systems
Anyone can learn the definitions of “drift” or “orchestration.”
But very few can
- Create an ML pipeline
- Deploy a model using Docker
- set up monitoring
- automate retraining
This is why practical MLOps experience sets you apart.
1. What Projects Should Beginners Build First?
Start with simple, structured projects that teach core workflows.
Here are the best beginner-friendly ones to build your MLOps foundation.
Beginner Project 1: Data Versioning With DVC
What you learn
- dataset tracking
- reproducible experiments
- linking DVC to cloud storage
- running pipelines
Key tasks
- Create a dataset folder
- version it with DVC
- track preprocessing steps
- push & pull data
This teaches you reproducibility, the heart of MLOps.
Beginner Project 2: Experiment Tracking With MLflow
What you learn
- logging metrics
- tracking model parameters
- comparing experiments
Key tasks
- train a simple model
- log accuracy & loss
- visualize experiments
- Register the best model
You now understand how ML experiments are managed in real teams.
Beginner Project 3: Containerising a Model With Docker
What you learn
- managing dependencies
- building Docker images
- running models inside containers
Key tasks
- Create a Dockerfile
- Add your Python environment
- expose an endpoint
- Run the container locally
This is your first step toward deployment.
Beginner Project 4: Deploying a Model With FastAPI
What you learn
- creating inference APIs
- request/response handling
- deploying model endpoints
Key tasks
- build a small FastAPI app
- load your trained model
- return predictions
- test using Postman or curl
This gives you a complete working ML API.
2. What Intermediate Projects Should You Build?
Once you understand the basics, move to more realistic, production-style projects.
Intermediate Project 1: End-to-End Training Pipeline (Airflow or Prefect)
Build an automated pipeline that:
- loads data
- preprocesses data
- trains the model
- evaluates results
- stores artifacts
This simulates real ML jobs in production.
Intermediate Project 2: CI/CD for ML Using GitHub Actions
Create automation for
- code linting
- unit tests
- Docker builds
- model validation
- automatic deployment
This demonstrates production-level ML engineering skills.
Intermediate Project 3: Model Monitoring + Drift Detection
Use tools like
- EvidentlyAI
- Prometheus
- Grafana
Monitor
- input distributions
- output quality
- latency
- drift alerts
This project is extremely valuable for resumes.
3. What Advanced or Portfolio Projects Should You Build?
These projects demonstrate true MLOps expertise.
Portfolio Project: Full MLOps Pipeline (Highly Recommended)
Build a complete system that includes
- data ingestion
- versioning
- training pipeline
- experiment tracking
- Dockerized model
- FastAPI endpoint
- CI/CD deployment
- monitoring dashboard
- drift detection
- automated retraining
If you build this, you will stand out instantly in interviews.
Bonus: LLMOps / RAG Pipeline Project (2025 Trend)
A strong, modern portfolio should include an LLM-based project.
Your project could include
- embedding generation
- vector database (Pinecone/FAISS)
- RAG-based answer generation
- logging hallucination rates
- monitoring vector recall
- deploying via BentoML
Professionals with this skill are in high demand right now.
4. Where Can You Find Realistic Project Ideas?
You don’t have to invent everything yourself.
Here are the best places:
GitHub (search “mlops project”, “mlops pipeline”)
Kaggle Datasets (use cases to automate pipelines)
HuggingFace (LLM projects + inference)
MLOps communities (Discord, MLOps.com)
Papers With Code (state-of-the-art ML systems)
These resources help you find industry-grade problems to solve.
5. What Counts As a “Portfolio-Ready” MLOps Project?
A strong project should include
- clear project structure
- pipeline automation
- Dockerized deployment
- monitoring dashboard
- README with architecture diagram
- real datasets
- code that runs end-to-end
This tells employers:
“I can build, deploy, and maintain ML systems — not just train them.”
Key Takeaways
- Start small with DVC, MLflow, and FastAPI
- Move to pipeline orchestration and CI/CD
- Finally, build an end-to-end automated system
- Add a modern LLMOps project for 2025 relevance
- Focus on reproducibility, automation, and monitoring
This is exactly how real MLOps engineers gain experience.
Which Certifications & Courses Actually Help in 2025?
Many beginners waste months collecting random certificates that don’t improve their skills or job prospects.
In MLOps, quality matters more than quantity.
This section focuses only on the certifications and courses that truly add value in 2025 — the ones hiring managers recognise and trust.
Why Certifications Matter (But Only the Right Ones)
The right certifications can help you
- Prove your skills
- stand out in applications
- qualify for cloud/MLOps roles
- demonstrate hands-on experience
- Validate your understanding of ML & DevOps fundamentals
But certifications alone won’t get you hired.
They must be paired with real projects (from Section 6).
1. Best MLOps-Focused Certifications (2025)
These certifications give the highest ROI for aspiring MLOps engineers.
1. Google Cloud Professional ML Engineer
Why it’s valuable
- Highly respected in the industry
- Covers ML development + deployment
- Includes monitoring & data pipelines
- Cloud-native MLOps workflows
Difficulty: Moderate to high
Ideal for: Mid-level learners
2. AWS Machine Learning Speciality
Why it’s valuable
- Deep dive into ML infrastructure
- Covers automation, scaling, and deployment
- Great for AWS-heavy companies
Difficulty: High
Ideal for: Intermediate learners
3. Azure AI Engineer Associate
Why it’s valuable:
- Enterprise-focused
- Strong coverage of ML lifecycle
- Good for Microsoft-based organisations
Difficulty: Moderate
Ideal for: Beginners to intermediate learners
4. Linux Foundation MLOps Certification (LF AI)
Why it’s valuable
- Vendor-neutral
- Pure MLOps content
- Covers Kubeflow, MLflow, containers, CI/CD
- Highly practical and future-proof
Difficulty: Beginner to intermediate
Ideal for: Students & MLOps beginners
2. Best Courses to Learn MLOps Skills (2025)
Below are only the top practical courses — no fluff, no outdated content.
1. Coursera: MLOps Specialisation (DeepLearning.AI)
Why it’s great
- Clear explanations
- Hands-on labs
- Covers CI/CD, TFX, and production ML
Perfect crash course for beginners.
2. Udacity: Machine Learning DevOps Engineer Nanodegree
Why it’s great
- Extremely practical
- Projects included
- One of the best MLOps curricula
More expensive, but highly valuable.
3. Microsoft Learn: MLOps with Azure ML
Why it’s great
- Free
- Covers pipelines and deployment
- Beginner-friendly
Ideal for students and self-learners.
4. YouTube + Open-Source Courses
Channels worth following
- MLOps Community
- Krish Naik
- DataTalks.Club
- Google Cloud Tech
These are excellent for staying updated with 2025 tools like
- LangChain
- vector databases
- LLMOps
- RAG pipelines
- Kubeflow 2.0
- BentoML 2.x
Certification Comparison Table
Certification | Focus Area | Difficulty | Best For |
Google ML Engineer | Cloud ML + MLOps | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Intermediate |
AWS ML Speciality | ML Infrastructure | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | Advanced |
Cloud + ML Ops | ⭐⭐⭐ | Beginners | |
Linux Foundation MLOps | Tools + Pipelines | ⭐⭐⭐ | Beginners/Intermediate |
Should You Get All These Certifications?
No. Pick one cloud certification + one MLOps specialisation.
Example
Linux Foundation MLOps + Google ML Engineer
or
Coursera MLOps Specialization + AWS ML Specialty
This combination makes you job-ready.
Where Should You Network to Grow Your MLOps Career?
Networking is one of the most underrated parts of becoming an MLOps engineer.
Many people study alone, build projects alone, and apply alone — which makes the journey slow and discouraging.
But here’s the good news
The MLOps community is one of the most open, helpful, and beginner-friendly tech communities.
You just need to know where to look.
This section shows you the best places to connect, learn, ask questions, and find opportunities in 2025.
Why Networking Matters for MLOps
Networking helps you
- learn from real engineers
- Get feedback on your projects
- understand hiring trends
- discover internship & job openings
- Stay updated with new tools (especially LLMOps!)
- join workshops, webinars, and hackathons
- Get mentorship and guidance
In many cases, networking is how people land their first MLOps job.
1. Best Online Communities for MLOps Engineers
These communities are active, supportive, and filled with industry experts.
MLOps Community (mlops.community)
Why it’s valuable
- Global community
- Weekly meetups
- Podcasts and workshops
- Great for beginners and professionals
This is the #1 community every MLOps learner should join.
DataTalks.Club
Why it’s valuable
- Free MLOps courses
- Practical discussions
- Strong Slack community
- Great for beginners
They also run “Machine Learning Zoomcamp” — one of the best free ML courses online.
r/MLOps (Reddit)
Why it’s valuable
- Tool comparisons
- DevOps + ML discussions
- Real-world case studies
Great for quick answers and learning industry trends.
LinkedIn MLOps Groups
LinkedIn groups help you
- Find MLOps job postings
- See what companies are hiring
- connect with recruiters
Search for keywords like:
“MLOps Engineer”, “ML Engineer”, “DevOps + ML”
LinkedIn is especially useful for showcasing your portfolio.
2. Discord Servers for MLOps & AI (2025 Hotspots)
Discord servers are more active than Slack for real-time chats, mentorship, and beginner support.
HuggingFace Discord
Great for
- LLMOps
- transformers
- deploying LLMs
- RAG pipelines
One of the most active AI communities in the world.
Weaviate, Pinecone & LangChain Discords
Best for
- vector databases
- LLM search
- embeddings
- production LLM apps
These communities are gold for learning modern AI engineering.
Cohere, OpenAI & AI Engineering servers
Perfect for LLMOps aspirants.
You’ll see project showcases, Q&A sessions, and dev support.
3. Networking Through Events, Meetups & Conferences
Meeting people in person accelerates your learning 10× faster.
MLOps World
One of the largest MLOps conferences.
Great for deep insights, company talks, and hiring events.
Google Developer Groups (GDG)
Local meetups include sessions on:
- ML
- MLOps
- Vertex AI
- Kubernetes
Great for beginners and cloud learners.
PyData Meetups
Useful for
- ML practice
- data engineering
- best practices for pipelines
These events often feature hands-on workshops.
AI/ML Hackathons (Kaggle, Devpost, AIcrowd)
Hackathons help you
- work on real problems
- meet developers
- build team projects
- learn version control & collaboration
Hackathons make your resume stand out instantly.
4. Following the Right People (Industry Leaders)
Following experts keeps you updated with trends, tool changes, and new MLOps best practices.
Recommended people
- Chip Huyen
- Demetrios Brinkmann
- Hamel Husain
- Andrew Ng
- MLOps Community leaders
- DataTalks.Club speakers
- HuggingFace engineers
- LangChain creators
These people share cutting-edge insights daily.
5. How to Make Networking Actually Work for You
Networking isn’t about sending random messages.
Here’s how to do it correctly:
Share your projects publicly
Post on
- GitHub
- X (formerly Twitter)
Even simple beginner projects can get noticed.
Ask for feedback, not jobs
People help more when you ask:
“Can you review my pipeline design?”
NOT
“Can you refer me to your company?”
Participate in discussions
Answer beginner questions.
Share your learning journey.
You’ll grow faster and be more visible.
Join at least one active community.
Focus > quantity.
Choose one from earlier and participate.
Key Takeaways
- Networking is how many MLOps beginners land interviews
- The MLOps community is very open and helpful
- Discord, Slack, LinkedIn, and meetups are the best platforms
- Share your projects and participate actively
- Surround yourself with people who work in MLOps
This will dramatically accelerate your learning and job search.
How Should You Start Your MLOps Journey Today? (Conclusion)
If you’ve read this far, you already know that MLOps is not just a skill — it’s a complete engineering discipline.
And in 2025, it is one of the most in-demand and future-proof careers in AI.
But here’s the part most learners get wrong:
They overthink the roadmap and under-practice the essentials.
MLOps becomes simple when you follow a structured, realistic path.
Let’s break down exactly how you can start today.
1. Begin With the Simple Skills (Don’t Rush Tools Yet)
Start with the basics
- Python
- Linux & Bash
- Git
- ML fundamentals
These give you the foundation to understand pipelines and deployments later.
2. Build Your First ML Model and Deploy It
A simple FastAPI + Docker deployment teaches you:
- packaging
- APIs
- reproducibility
- debugging
This is your first “real” MLOps project.
3. Learn the Core MLOps Tools (One at a Time)
Prioritise tools that appear in job descriptions:
- DVC
- MLflow
- Docker
- GitHub Actions
- Airflow or Prefect
- Kubernetes basics
Don’t try to learn everything at once — build gradually.
4. Create a Real End-to-End Project for Your Portfolio
This is your ticket to interviews.
Your project should include:
- data versioning
- training automation
- experiment tracking
- deployment
- monitoring
- drift detection
- retraining pipeline
This single project shows employers you can run ML in production, not just train models.
5. Add One LLMOps or RAG Project (Huge Demand in 2025)
Modern MLOps now includes LLM operations.
Build a project that uses:
- vector databases
- embeddings
- retrieval pipelines
- LLM inference
- logging + monitoring
This makes your profile stand out immediately.
6. Join an MLOps Community and Showcase Your Work
Don’t learn alone.
Share your progress on:
- GitHub
- Discord communities
- MLOps Slack groups
Posting even simple projects builds your visibility and credibility.
7. Apply for Internships, Junior Roles, and Open-Source Projects
Many beginners underestimate the power of:
- contributing to MLflow / DVC
- joining open-source RAG projects
- applying to junior DevOps/ML roles
- taking freelance API deployment gigs
Small steps → real-world experience → stronger resume.
Final Takeaway
You do not need to learn everything at once.
You do not need all the tools.
And you definitely do not need to be a math genius.
Becoming an MLOps engineer is all about:
learning the essentials, building real projects, and improving step by step.
If you follow the roadmap in this blog, you will be ahead of 90% of learners — and well on your way to a high-growth AI career.
Ready to Start Your MLOps Career?
Here’s your simple, actionable starting checklist:
- Learn Python
- Learn ML basics
- Learn Docker & Git
- Build your first ML API
- Learn DVC + MLflow
- Build an automated pipeline
- Deploy your model
- Set up monitoring
- Add an LLMOps project
That’s it.
Follow this consistently for a few months, and you will be MLOps-job ready.
FAQs
MLOps can seem complex because it mixes ML, DevOps, and data engineering.
But if you learn step by step — starting with Python, Docker, and ML basics — it becomes manageable.
You don’t need to be a software expert, but you must know:
- Python
- Bash basics
- Git commands
These cover 80% of beginner MLOps tasks.
For consistent learners
- 3–4 months → beginner-level
- 6–9 months → job-ready
- 12+ months → advanced MLOps engineer
Keeping a regular study schedule helps a lot.
Yes.
You can start with
- Python basics
- ML fundamentals
- Git + Docker
Then gradually move to orchestration, deployment, and monitoring.
Yes — at least the basics
- model training
- evaluation metrics
- ML libraries
You don’t need deep math, but you must understand how ML models behave.
No.
Learn only the DevOps essentials first
- Linux
- Docker
- CI/CD fundamentals
You can learn deeper DevOps concepts later.
The core 2025 toolset includes
- DVC (versioning)
- MLflow (tracking)
- FastAPI (deployment)
- Docker (packaging)
- Kubeflow / Airflow (pipelines)
- EvidentlyAI (monitoring)
All is good, but in 2025
- AWS = Infrastructure-heavy roles
- GCP = ML & AI-first workflows
- Azure = Enterprise-focused MLOps
Choose based on your job region or preference.
Not at the beginner level.
But for advanced roles, yes, because most ML systems run on Kubernetes clusters.
- ML Engineers build models.
- MLOps Engineers deploy, monitor, and maintain them.
Both roles overlap, but MLOps focuses more on automation and reliability.
LLMOps is MLOps for large language models.
It covers
- prompt engineering
- vector databases
- RAG pipelines
- cost optimization
- hallucination detection
This skill is rapidly becoming essential.
RAG = Retrieval-Augmented Generation.
It combines
- LLM
- Vector database
- Document retrieval
It improves the accuracy and grounding of LLM-generated answers.
You need only a basic understanding of
- algebra
- probability
- ML metrics
Most work involves automation, coding, and pipelines — not deep math.
On average (global ranges)
- Entry level: $70k – $110k
- Mid-level: $110k – $160k
- Senior/Lead: $160k – $220k+
LLMOps roles often pay higher.
No.
Many MLOps engineers are self-taught.
What matters more:
- GitHub projects
- portfolio
- real deployment experience
- Understanding pipelines & automation
The best project is an end-to-end ML pipeline, including:
- data ingestion
- versioning
- training
- experiment tracking
- Docker deployment
- CI/CD
- monitoring
- automated retraining
With tools like
- Prometheus
- Grafana
- EvidentlyAI
Monitoring focuses on: - latency
- errors
- drift
- accuracy drops
- hallucinations (LLMs)
The top languages are
- Python (dominant)
- Go (for infra-heavy systems)
Bash (automation)
Others like Java, Rust, or C++ appear in specific roles, but Python is enough for 90% of beginners.
Absolutely.
In fact, LLMs increased the importance of MLOps because large models require:
- monitoring
- vector databases
- GPU orchestration
- scaling
- optimization
MLOps is evolving into AI Ops + LLMOps.
Start with this simple plan
- Learn Python
- Learn ML basics
- Learn Docker + Git
- Build simple ML APIs
- Learn DVC + MLflow
- Build a pipeline with Airflow or Prefect
- Learn Kubernetes basics
- Create one end-to-end portfolio project
This roadmap works for beginners, students, and working professionals.
