Neural Networks for Generative AI: The Complete 2026 Guide
Introduction
1. What Will You Learn About Neural Networks for Generative AI in This Guide?
Generative AI has become one of the most transformative technologies of the decade, and as we approach 2026, its impact is only accelerating. In this guide, you’ll learn the foundations that make generative AI work—specifically the neural networks that power today’s tools, models, and applications.
By the end of this guide, you will clearly understand
- What generative AI is and how it works behind the scenes
- The neural network architectures used for generative tasks
- How GANs, VAEs, and RNNs compare
- Key algorithms that make these models learn and generate content
- Real-world applications across industries in 2026
- Ethical challenges and how to learn generative AI the right way
This guide takes you from beginner-friendly explanations to professional-level insights—without overwhelming you with jargon.
2. Why Is Generative AI So Important as We Enter 2026?
Generative AI is no longer limited to research labs or tech giants. It is now deeply integrated into
- Education — personalized learning, automated content generation
- Healthcare — medical imaging, protein generation
- Entertainment — music, video, 3D character creation
- Business — marketing copy, code generation, product design
- Cybersecurity — synthetic data for safer testing
In 2026, generative AI is also becoming
- More multimodal — generating text, images, audio, and video together
- More efficient — running on smaller devices with optimized networks
- More regulated — with global AI safety standards emerging
Understanding neural networks allows you to grasp why these systems work—and how you can use them in your own career or projects.
3. Who Should Read This Guide?
This blog is designed for three primary groups:
1) Students & Beginners
If you’re just starting, you’ll find clear explanations, simple examples, and analogies that make complex ideas easier to understand.
2) Working Professionals
Engineers, designers, marketers, analysts, and educators will learn how neural networks influence the tools they use every day.
3) Non-Technical Learners
You don’t need a math or coding background—this guide avoids unnecessary complexity and focuses on real understanding.
4. How Is This Guide Structured and How Can You Use It Effectively?
To make learning easier, each section answers a specific question—the same way you might search on Google.
You’ll find
- Tables for comparing neural network types
- Bulleted summaries for quick reading
- Examples from 2026 technologies
- Actionable learning paths
- Practical explanations without fluff
Feel free to
- Read it step-by-step, or
- Jump to sections that interest you the most
This guide is built to be both a learning roadmap and a reference document you can revisit anytime.
What Is Generative AI and Why Does It Matter Today?
1. What Do We Mean by “Generative AI”?
Generative AI refers to a category of artificial intelligence models designed to create new data, not just analyze existing data. Instead of giving answers or predictions only, generative AI can produce
- Images
- Text
- Music
- Videos
- Code
- 3D models
- Synthetic datasets
The key idea
Generative AI learns the patterns in data and uses those patterns to produce original, realistic outputs.
This shift—from analysis to creation—is why generative AI has become so influential across industries.
2. How Does Generative AI Actually Work in Simple Terms?
Generative AI works by learning the distribution of data. Think of it like this:
If you show a model 10 million images of cats, it learns:
- Common shapes
- Fur textures
- Colors
- Positions
- Background patterns
Then the model can generate a new cat image that never existed before but looks believable.
The process involves
- Training a neural network on large datasets
- Learning patterns and compressing them into a latent space
- Generating new samples using that learned space
This is why models like GPT, Stable Diffusion, and Midjourney can generate creative content on demand.
3. What Are the Core Components Behind Generative Systems?
Generative AI systems typically include several foundational components:
1. Neural Networks
The engines that learn from data.
Different architectures (GANs, VAEs, RNNs, diffusion models) serve different generative purposes.
2. Latent Space
A compressed representation of knowledge.
Think of it as the “imagination space” where concepts blend.
3. Training Algorithm
Methods like gradient descent, backpropagation, and variational inference help models improve.
4. Loss Functions
Metrics that tell the model whether its output is good or bad.
Example
- GANs use adversarial loss
- VAEs use reconstruction loss + KL divergence
5. Data
The fuel of generative AI.
High-quality, diverse datasets lead to better and more ethical outputs.
4. Where Do We Use Generative AI in 2026? (Industries & Real Examples)
By 2026, generative AI will have expanded into nearly every industry. Here are the most significant use cases:
Education
- AI tutors generating personalized lessons
- Automated quizzes, visualizations, and study guides
- Assistive tools for teachers to design curriculum
Creative & Design Industries
- Video generation for advertising
- AI-powered image and 3D model creation
- Music and audio production
Business & Productivity
- Automated report writing and content generation
- UX design generation from simple prompts
- Customer service chatbots with human-like responses
Healthcare
- Synthetic medical images for safer AI training
- Protein and drug structure generation
- Personalized treatment simulations
Science & Research
- Molecule generation
- Climate and physics simulations
- Automated hypothesis generation
Cybersecurity
- Generating synthetic attack scenarios
- Simulating threat environments
Manufacturing & Robotics
- AI-generated prototypes
- Simulation of industrial processes
Generative AI is shaping a world where creative and analytical tasks blend seamlessly with automation and augmentation.
How Do Neural Networks Power Generative AI?
1. What Exactly Is a Neural Network?
A neural network is a computer model inspired by how the human brain works. It uses interconnected layers of nodes (neurons) to process and learn from information.
Think of it as a pattern-recognition engine.
When you train a neural network on data:
- It identifies relationships
- Learns features
- Builds internal representations
- Uses those representations to generate or classify content
In generative AI, neural networks don’t just recognize patterns—they learn to recreate them.
2. How Is a Neural Network Structured (Layers, Neurons, Weights)?
A neural network typically includes three main types of layers:
1. Input Layer
Where the model receives data — images, text, audio, etc.
2. Hidden Layers
Where most learning happens.
These layers
- Transform inputs
- Detect patterns
- Build abstractions
- Compress information into latent features
The more hidden layers a network contains, the “deeper” the model becomes.
This is why modern AI is called deep learning.
3. Output Layer
Produces the final result, such as:
- An image
- A sentence
- A probability
- A numerical value
Each connection between neurons has a weight that determines how strongly information flows.
Training = adjusting these weights until the model learns an accurate representation.
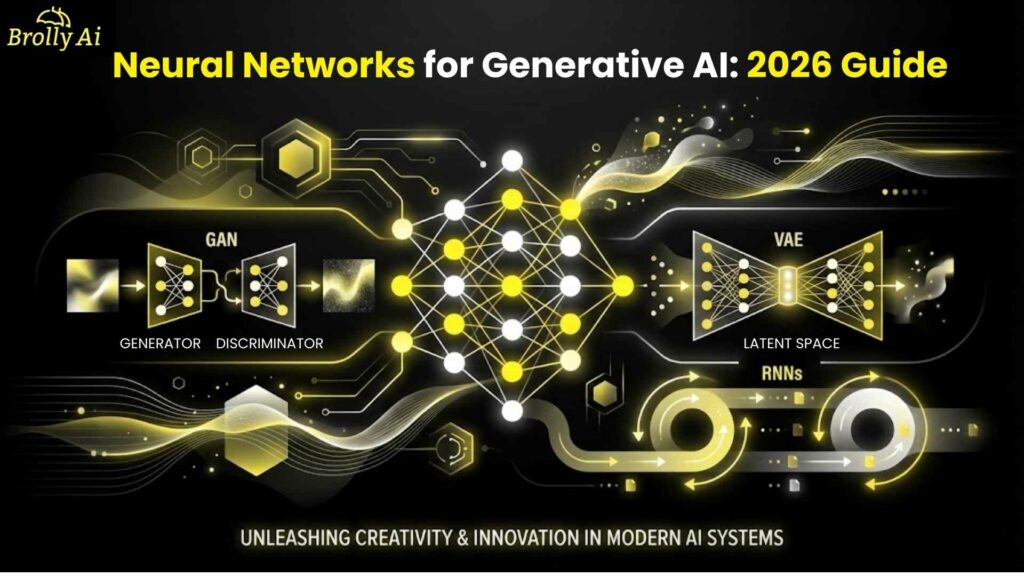
3. What Types of Neural Networks Are Most Important for Generative AI?
Different generative tasks require different neural architectures. The most important types for generative AI include:
- Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs) — Simple structure, used for basic encoding/decoding
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) — Excellent for images and spatial data
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) — Used for sequences like text and music
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) — Extremely good at generating realistic images
- VAEs (Variational Autoencoders) — Great for structured latent space and reconstruction
- Transformers — The dominant architecture for text, image, and multimodal generation
In 2026, the Transformer remains the leading architecture for large-scale generative models because it handles long-range dependencies and parallel computation efficiently.
4. Why Are Activation Functions Essential for Learning?
Activation functions determine whether a neuron should activate.
Without them, a neural network would behave like a simple linear system — unable to learn complex patterns.
Common activation functions include:
Activation Function | Key Feature | Used In |
ReLU | Fast, simple, reduces vanishing gradients | Deep networks, CNNs |
Sigmoid | Compresses output to 0–1 | Binary classification, logistic layers |
Tanh | Works well for normalized data | RNNs |
Softmax | Converts values into probabilities | Output layers |
For generative models
- GANs often use LeakyReLU
- VAEs commonly use ReLU or Sigmoid
- RNNs and LSTMs rely on Tanh and Sigmoid gates
These functions introduce non-linearity, enabling models to learn patterns such as shapes, textures, grammar, and rhythm.
5. How Do We Train Neural Networks Efficiently?
Training involves helping the network reduce its loss — the difference between predicted and real values.
Key steps include:
1. Forward Propagation
Data flows through the network and produces an output.
2. Compute Loss
Loss function compares output vs. ground truth.
Examples
- GANs → adversarial loss
- VAEs → reconstruction loss + KL divergence
- RNNs → sequence prediction loss
3. Backpropagation
Gradients are calculated to determine how much each weight contributed to the error.
4. Gradient Descent Optimization
Weights update using algorithms such as:
- Adam
- SGD
- RMSProp
- AdamW (popular in 2026)
5. Regularization
Helps prevent overfitting using:
- Dropout
- Weight decay
- Data augmentation
Efficient training is essential because generative AI models often contain millions or billions of parameters.
What Types of Neural Networks Are Used in Generative AI?
1. Why Do Different Generative Tasks Need Different Neural Networks?
Generative AI is not a single task — it covers text, images, audio, video, code, style transfer, sequence prediction, and more.
Each type of data has unique properties:
- Images → spatial patterns
- Text → sequential patterns
- Audio → continuous temporal signals
- 3D models → geometric structures
Because of these differences, a single neural network architecture cannot handle everything efficiently.
This is why generative AI uses specialized architectures optimized for specific data types.
For example
Generative Task | Best-Suited Neural Network |
Image generation | GANs, VAEs, CNN-based diffusion models |
Text generation | RNNs (legacy), LSTMs, Transformers |
Audio generation | RNNs, WaveNet, diffusion models |
Style transfer | CNNs |
Sequence prediction | RNNs, GRUs, LSTMs |
Latent representation learning | VAEs |
Understanding these differences helps beginners choose the right model for their projects.
2. Which Neural Network Architectures Are Commonly Used in Generative AI?
The major types used in 2026 include:
1. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Two competing networks (generator vs. discriminator) create realistic images, videos, or data.
Best for
- Image synthesis
- Deepfake generation
- Art and style generation
- Super-resolution
2. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
Encoder–decoder structure that learns a structured latent space.
Great for interpolation and controlled generation.
Best for
- Medical image synthesis
- Data compression
- Anomaly detection
- Feature extraction
3. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
Designed for sequence generation such as text, audio, or time-series data.
Variants include
- Vanilla RNN
- GRU
- LSTM
Best for
- Music generation
- Language modeling (early models)
- Sequential forecasting
4. Transformers
The dominant architecture for modern generative models, including GPT-like systems.
Transformers excel at
- Long-range dependencies
- Multimodal generation
- Large-scale training
5. Diffusion Models (honorable mention)
Not in your list, but important in 2026.
They generate content by gradually removing noise.
Used in
- Midjourney
- Stable Diffusion
- DALL·E 3+
Even though not the focus of this article, diffusion models have reshaped AI generation and often combine with neural networks like U-Nets (CNN-based).
3. How Do GANs, VAEs, and RNNs Differ?
Here’s a simple comparison:
Feature | GANs | VAEs | RNNs |
Best for | Realistic image creation | Controlled generation & reconstruction | Sequence generation |
Output style | Sharp, realistic | Smooth, structured | Temporal patterns |
Training difficulty | Hard | Moderate | Easy–medium |
Mode collapse risk | High | Low | None |
Latent space | Unstructured | Structured | Not typical |
Used in | Images, video | Medical, robotics, and embeddings | Text, music |
Summary
- GANs = realism
- VAEs = structure and latent control
- RNNs = sequence prediction and generation
Each network has a unique strength that supports different areas of generative AI.

What Are Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and How Do They Work?
1. What Are GANs and Why Are They a Generative AI Breakthrough?
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), introduced by Ian Goodfellow in 2014, revolutionized the world of generative AI by enabling machines to create incredibly realistic images, videos, and synthetic data.
GANs gained popularity because they can:
- Generate high-resolution images
- Mimic artistic styles
- Create deepfakes
- Enhance image quality (super-resolution)
- Produce data without labeled training sets
The secret behind GANs is a unique adversarial learning framework where two networks battle each other to improve performance. This dynamic leads to stunning outputs that resemble real-world data.
2. What Does the Generator Do?
The Generator is the creative artist.
Its job is to take random noise (e.g., a vector of numbers) and transform it into something that looks real—an image, audio sample, or another form of data.
The generator
- Learns the distribution of the training data
- Produces synthetic samples
- Tries to fool the discriminator
When trained effectively, the generator becomes extremely good at imitating real data patterns.
3. What Does the Discriminator Do?
The Discriminator is the critic.
Its job is to evaluate input data and decide whether it is:
- Real (from the dataset)
- Fake (produced by the generator)
The discriminator
- Learns the features of genuine data
- Provides feedback to the generator
- Helps improve the quality of fake samples
This adversarial relationship pushes both networks to become better over time.
4. How Does the Adversarial Training Process Work?
GAN training works like a competitive game:
Step 1: The Generator produces fake data
It starts with random noise → generates an image.
Step 2: Discriminator receives both real and fake data
It tries to classify them correctly.
Step 3: Compute losses
- The generator wants the discriminator to think fake data is real
- Discriminator wants to detect fake data correctly
Step 4: Backpropagation updates both networks
- Generator improves its output
- Discriminator improves its detection
Step 5: Repeat until outputs look real
Over thousands of training steps, the generator becomes skilled at “fooling” the discriminator.
This process is known as minimax optimization—a push-pull dynamic where both networks improve continuously.
5. Where Are GANs Used in Industry (2026 Examples)?
GANs remain extremely important in 2026, powering many creative and commercial applications.
Creative and Digital Art
- AI-generated paintings
- Character design for games and films
- Concept art generation
Image Enhancement
- Super-resolution
- Removing noise or blur
- Restoring old photos and videos
Healthcare
- Generating synthetic medical images for training
- Privacy-preserving data augmentation
E-commerce & Marketing
- Generating product photos
- Creating personalized ad visuals
Deepfakes & Media Production
- Video face-swapping
- Voice mimicry (in combination with audio models)
Cybersecurity & Defense
- Synthetic data for safe model training
- Simulation of adversarial attacks
GANs have become a standard tool for companies working in design, imaging, virtual try-on, and synthetic data generation.
6. What Are the Challenges and Limitations of GANs?
Despite their power, GANs come with several challenges:
1. Training Instability
GANs are notoriously difficult to train because the generator and discriminator must stay balanced.
If one becomes too strong, the other collapses.
2. Mode Collapse
The generator might create only a few similar outputs rather than diverse ones.
3. High Computational Cost
Training GANs requires powerful GPUs and large datasets.
4. Ethical Risks
GANs can create deepfakes that misuse identities or spread misinformation.
5. Sensitive to Hyperparameters
Small changes in learning rates, loss functions, or network depth can break training.
Despite these challenges, GANs continue to evolve with improved architectures such as StyleGAN, CycleGAN, and BigGAN.
What Are Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) and Why Do They Matter?
1. What Makes a VAE Different from a Regular Autoencoder?
A traditional autoencoder compresses input data into a smaller representation and then reconstructs it.
However, it learns exact mappings, which limits creativity.
A Variational Autoencoder (VAE) adds a powerful twist:
- Instead of learning a single representation, it learns a distribution of possible representations.
- This allows VAEs to sample new variations from that distribution.
In simple terms:
A regular autoencoder copies; a VAE creates.
This makes VAEs ideal for controlled, smooth, and meaningful generation of new data.
2. How Do VAEs Learn Latent Representations?
VAEs map input data into a latent space, which is a compressed vector representing the essential features of the data.
Unlike GANs, where the latent space is often unstructured, VAEs produce a smooth, continuous latent space, allowing:
- Easy interpolation between data points
- Controlled manipulation of features
- Better understanding of underlying patterns
Example:
If you encode images of faces, you can move through latent space to:
- Change hair length
- Adjust lighting
- Modify facial expressions
This is why VAEs are hugely valuable in research, robotics, and medical imaging.
3. What Are the Key Components of a VAE?
A VAE consists of two main parts:
1. Encoder
Takes input → outputs two vectors:
- Mean (μ)
- Variance (σ²)
These represent a probability distribution for the latent variables.
2. Latent Space
A continuous, structured representation where sampling happens.
3. Decoder
Takes a sampled latent vector → reconstructs the input.
The encoder compresses, the decoder reconstructs, and together they create new, realistic variations of data.
4. What Is Variational Inference and Why Is It Important?
VAEs use variational inference to approximate complex probability distributions.
Here’s why it matters
- Real-world distributions are too complicated to model directly
- Variational inference provides a way to approximate them
- The KL divergence term ensures the latent space stays smooth and structured
This allows VAEs to generate:
- Diverse samples
- Continuous transformations
- Realistic but controlled outputs
In contrast, GANs focus more on realism and less on structure.
5. How Are VAEs Trained and Optimized?
Training a VAE involves minimizing a loss function made of two components:
1. Reconstruction Loss
Ensures output resembles input.
Common choices
- Mean squared error
- Cross-entropy loss
2. KL Divergence Loss
Ensures latent variables follow a normal distribution.
The combined objective gives VAEs:
- Stability in training
- Control over latent space
- Smooth generative capabilities
This makes them easier to train than GANs and more interpretable for scientific applications.
How Do Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) Enable Sequence Generation?
1. Why Are RNNs Useful for Sequence-Based Generative Tasks?
Many forms of data—such as text, speech, music, time-series, and sensor signals—share one property:
They unfold over time.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) were designed specifically to handle this.
What makes them unique is their ability to:
- Remember previous inputs
- Maintain context across sequences
- Generate outputs step-by-step
This memory capability allows RNNs to generate:
- Sentences that flow naturally
- Melodies that follow musical structure
- Predictive sequences like stock prices
Before Transformers dominated text generation, RNNs were the backbone of early language models.
2. How Does Sequence Generation Work Step-by-Step?
RNNs generate sequences one element at a time.
Here’s the typical process:
Step 1: Input the first token
For example, in text generation, the first word is fed into the network.
Step 2: RNN updates its hidden state
The hidden state stores memory of past information.
It captures patterns like:
- Grammar
- Rhythm
- Context
- Order
Step 3: The next element is predicted
The model outputs the next token (word, note, etc.).
Step 4: The generated token becomes the next input
The loop repeats.
Step 5: The process continues until the sequence ends
This cyclical process allows the model to build long structures like paragraphs, melodies, or sequences of motions.
3. What Does an RNN Architecture Look Like?
An RNN has three main components:
1. Input Layer
Receives each element in the sequence one step at a time.
2. Hidden Layer (Recurrent Layer)
The key innovation:
This layer connects back to itself, allowing information to persist across time steps.
3. Output Layer
Predicts the next element in the sequence.
Basic RNN equation:
Hidden state = f(previous hidden state + current input)
This loop is what enables temporal understanding.
4. What Key Features Support RNN Performance in Generative AI?
RNNs include design features that make them well-suited for sequential tasks:
1. Memory Mechanism
The hidden state stores important sequence information.
2. Parameter Sharing
The same weights are reused across time steps, reducing complexity.
3. Stepwise Output
Generates each part of the sequence one unit at a time.
4. Flexibility With Input Lengths
Works with variable-length sequences, unlike fixed-size neural networks.
These features made RNNs foundational for early generative tasks like:
- Machine translation
- Chatbots
- Music generation
- Speech modeling
5. How Do Vanilla RNNs, LSTMs, and GRUs Compare?
To overcome limitations like vanishing gradients, improved versions of RNNs were developed.
Here’s a simple comparison:
Model Type | Key Feature | Strengths | Weaknesses |
Vanilla RNN | Basic recurrence | Simple, fast | Forgets long-term info, unstable |
LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) | Uses gates to control memory | Excellent long-term memory | Heavier, more parameters |
GRU (Gated Recurrent Unit) | Simplified LSTM | Faster, efficient | Slightly less expressive |
Vanilla RNN
- Good for short sequences
- Not ideal for complex tasks
LSTM
- Best for long sequences
- Great for text and music generation
- Still used in robotics and healthcare modeling
GRU
- Faster than LSTM
- Strong performance with fewer parameters
- Often used in real-time applications

What Are the Key Algorithms That Drive Generative AI?
Generative AI models depend on algorithms that allow them to learn patterns, optimize performance, and produce new content. These algorithms are the mathematical engine behind neural networks.
1. Which Generative Algorithms Matter Most in 2026?
Several algorithms remain central to generative AI, even as the field evolves. The most important include:
1.1 Backpropagation
The core algorithm for training neural networks.
It computes gradients that update weights.
1.2 Gradient Descent Variants
Optimize model parameters to reduce loss.
Popular versions in 2026 include:
- AdamW
- RMSProp
- Nesterov Momentum
- Lion Optimizer (gaining traction)
1.3 Variational Inference
Used heavily in VAEs to estimate distributions.
1.4 Adversarial Training
The “game” between generator and discriminator in GANs.
1.5 Sampling Algorithms
Essential for generating new data from models.
Includes
- Ancestral sampling
- Temperature sampling
- Top-k and top-p sampling (especially in text generation)
1.6 Latent Space Manipulation
Used to navigate and control generative outputs.
Example: editing face attributes in latent space.
1.7 Attention Mechanisms
While more common in Transformers, they influence generative models by focusing on important features across sequences.
These algorithms together form the backbone of modern generative AI capabilities.
2. How Do Backpropagation and Gradient Descent Enable Learning?
Backpropagation and gradient descent work as a feedback loop that teaches neural networks how to improve.
Backpropagation Steps
- Network makes a prediction
- Loss is calculated
- Gradients are computed layer by layer
- Gradients flow backward through the network
- Weights are adjusted to reduce future error
Gradient Descent:
Changes weights in the direction that reduces loss the fastest.
Think of it like climbing down a hill to reach the lowest point (minimum error).
This process is repeated thousands or millions of times during training.
Without these algorithms, networks would never learn patterns or generate coherent outputs.
3. What Is Latent Space and Why Is It So Important?
Latent space is a compressed representation of data inside a generative model.
Imagine compressing a high-resolution image into a small vector of numbers that still captures
- Shape
- Style
- Texture
- Attributes
Latent space enables:
Feature editing
Example
- Making a face smile
- Changing lighting
- Adjusting color tones
Interpolation
Moving smoothly between two points in latent space creates transformations like:
- Face morphing
- Style blending
- Concept transitions
Controlled generation
VAEs specialize in structured latent spaces.
GANs can learn meaningful latent spaces too (e.g., StyleGAN).
Latent space is the reason generative AI feels creative.
4. Which Optimization Techniques Improve Generative Models?
Several modern optimization strategies help stabilize and improve generative models:
4.1 Batch Normalization
Helps stabilize GAN training and speeds up convergence.
4.2 Dropout
Reduces overfitting by turning off random neurons during training.
4.3 Weight Decay
Prevents models from becoming too complex.
4.4 Gradient Penalty
Used in WGAN-GP to stabilize adversarial training.
4.5 Learning Rate Scheduling
Automatically adjusts learning rate during training to prevent divergence.
4.6 Early Stopping
Stops training when further learning provides no improvement.
4.7 Data Augmentation
Increases dataset diversity, essential for image-based generative models.
Together, these techniques significantly enhance training stability and output quality.
How Do GANs, VAEs, and RNNs Compare?
Generative AI uses multiple neural network architectures, each with its own strengths. Understanding their differences helps you choose the right model for your project.
Below is a clear, concise comparison across the most important dimensions.
1. Comparison Table: GANs vs. VAEs vs. RNNs
Feature / Criteria | GANs | VAEs | RNNs (LSTM/GRU) |
Primary Purpose | Generate realistic images and media | Learn structured latent spaces; generate smooth outputs | Generate sequential data such as text, music, speech |
Output Quality | Sharp, high-quality visuals | Slightly blurry but consistent | Depends on sequence structure, not visual quality |
Training Difficulty | Hard (unstable, adversarial) | Easier than GANs | Moderate; simpler than both GANs and VAEs |
Latent Space | Unstructured (unless using upgrades like StyleGAN) | Smooth & interpretable | Not typically used |
Best For | Image synthesis, art, deepfakes, super-resolution | Medical imaging, robotics, interpolation, representation learning | Text generation, audio modeling, time-series prediction |
Strengths | High realism, creative diversity | Stable training, controllable outputs | Handles long-term patterns in sequences |
Weaknesses | Mode collapse, instability, and high computational cost | Blurry outputs, limited realism | Struggles with very long sequences; slower than Transformers |
Examples (2026) | StyleGAN3+, BigGAN | VQ-VAE, Beta-VAE | LSTM chatbots, GRU audio models |
Typical Use Cases | Advertising, entertainment, face generation | Research, healthcare, anomaly detection | IoT data, music generation, language tasks |
2. Which Model Should You Choose for Your Project?
Choose GANs if you need
- High-quality images
- Style transfer
- Realistic media
- Creative visual generation
Examples
AI art platforms, virtual try-on systems, and synthetic product photography.
Choose VAEs if you need:
- A structured latent space
- Smooth transitions between outputs
- Stable training
- Controlled generation
Examples
Medical imaging, robotics, compression, anomaly detection.
Choose RNNs if you need
- Sequences that follow time-based patterns
- Audio or music generation
- Lightweight generative tasks
- Real-time sequence modeling
Examples
Predictive typing, melody generation, and IoT signal prediction.
3. How Do These Models Work Together in Modern Systems?
In 2026, many advanced generative AI systems combine multiple architectures:
- VAE + GAN Hybrid
Produces outputs that are both structured and realistic.
Used in image editing and face synthesis. - RNNs + Transformers:
Used in voice assistants and speech generation. - GANs + Diffusion Models:
Combines GAN sharpness with diffusion stability.
These hybrid systems deliver better quality, stability, and control than any single architecture alone.
4. Summary of Differences in One Sentence
- GANs generate realism,
- VAEs generate structure,
- RNNs generate sequences.
How Is Generative AI Used in Real-World Industries?
Generative AI has moved far beyond research labs. By 2026, it will be a practical tool transforming workflows, accelerating creativity, and making complex tasks more accessible across industries.
Below are the major sectors where generative AI—powered by neural networks—is having the biggest impact.
1. How Is Generative AI Transforming Education and Skill Development?
Education is one of the fastest-growing applications for generative AI. Neural network–driven tools now help both learners and teachers create, analyze, and personalize content.
AI-Powered Personalized Learning
- Adaptive study plans
- Dynamic quizzes based on skill level
- Automatic feedback on essays and code
- Learning paths tailored to strengths and weaknesses
Content Generation for Educators
- Auto-generated worksheets, tests, and explanations
- Personalized reading materials based on grade level
- Visual explanations created by AI image models
Virtual Tutors and Assistants
These systems use transformer-based and RNN-based models to:
- Explain concepts in simple terms
- Offer step-by-step problem-solving
- Provide instant help, 24/7
Skill Development and Workforce Training
Companies use generative AI to
- Simulate real-world job tasks
- Produce training videos and scenarios
- Generate practice datasets
Generative AI makes learning more engaging, interactive, and personalized—an educational revolution.
2. How Are Companies Using Generative AI in 2026?
Businesses across all sectors now rely on generative AI for automation, creativity, and decision-making.
Marketing and Content Creation
- AI-generated social media posts
- Personalized ad creatives
- Automated video creation
- Product descriptions written at scale
GANs and VAEs are especially useful in creating product images, virtual try-ons, and ad visuals.
Software Development
Generative models help developers by:
- Suggesting code
- Explaining errors
- Auto-generating documentation
- Creating synthetic data for testing
RNNs and Transformers contribute heavily to these tools.
Product Design and Prototyping
Manufacturers now use generative models to:
- Auto-generate 3D prototypes
- Explore multiple design variations
- Simulate the physical behavior of products
Diffusion models combined with CNNs lead this space.
Customer Service
AI assistants powered by neural networks can:
- Understand customer queries
- Generate helpful answers
- Personalize responses based on context
This reduces wait times and improves user experience.
3. What Are the Most Impactful Use Cases Across Major Industries?
Here is a quick snapshot of how different industries leverage generative AI:
Industry | Key Generative AI Uses | Network Types Involved |
Healthcare | Synthetic medical images, drug discovery, predictive modeling | VAEs, GANs |
Finance | Fraud simulation, risk modeling, synthetic transaction data | RNNs, Transformers |
Entertainment | Video generation, scriptwriting, character design | GANs, RNNs |
Retail | Virtual try-on, AI-generated product photos | GANs |
Manufacturing | 3D design generation, simulation | VAEs, diffusion models |
Cybersecurity | Attack simulation, defense training | GANs |
Transportation | Route generation, autonomous driving simulation | RNNs, VAEs |
Generative AI is not just automating tasks—it is creating entirely new ways of working, enabling industries to innovate faster than ever before.
What Challenges and Ethical Concerns Should We Consider?
Generative AI is powerful, but it also introduces complex challenges—both technical and ethical. As models become more capable in 2026, responsible use becomes more critical than ever.
Below are the key issues you should understand.
1. What Technical Challenges Still Limit Generative Models?
Even with breakthroughs in 2026, generative neural networks face limitations:
1.1 Training Instability
Models like GANs are notoriously unstable
- Generator and discriminator must stay balanced
- Small parameter changes can break training
- Mode collapse may occur (limited output diversity)
1.2 High Computational Requirements
Large generative models require:
- Expensive GPUs or TPUs
- Long training times
- Massive datasets
This creates barriers for small organizations and individual learners.
1.3 Data Quality Issues
Generative AI depends heavily on the quality of its training data. Poor datasets lead to:
- Unreliable outputs
- Bias and inaccuracies
- Overfitting
1.4 Difficulty in Evaluation
Evaluating generated content is hard because:
- There’s no absolute “correct” answer
- Realism is subjective
- Metrics like FID, BLEU, and perplexity have limitations
1.5 Generalization Limits
Models may struggle with
- Novel situations
- Unexpected prompts
- Edge-case behavior
Even advanced models are not fully “creative”—they remix learned patterns.
2. What Ethical Risks Come with Generative AI (Deepfakes, Bias, IP Issues)?
Generative AI’s ability to mimic, fabricate, and automate raises serious ethical concerns:
2.1 Deepfakes and Misuse
GAN-powered deepfakes can
- Impersonate people
- Spread misinformation
- Manipulate public opinion
This poses threats to privacy, trust, and security.
2.2 Bias in Generated Outputs
If training data contains bias, models may reproduce:
- Stereotypes
- Discriminatory patterns
- Inaccurate representations
Bias reflects the data, not the technology — but the consequences are real.
2.3 Intellectual Property (IP) and Copyright Issues
Key concerns include
- Models generating content similar to copyrighted works
- Training on datasets without explicit permission
- Gray areas around AI-generated art and ownership
In 2026, global governments are actively working on clearer regulations.
2.4 Privacy Risks
Models trained on sensitive data may accidentally:
- Reconstruct personal information
- Reveal medical or financial attributes
- Generate outputs that resemble real individuals
Differential privacy and synthetic data help mitigate these risks.
2.5 Job Displacement Fears
While generative AI creates opportunities, it also automates:
- Graphic design
- Copywriting
- Data analysis
- Entry-level programming tasks
The solution isn’t resisting AI—it’s upskilling to work alongside it.
3. How Can Individuals and Organizations Use Generative AI Responsibly?
Responsible use ensures innovation without harm.
Here are key practices:
3.1 Transparency
Disclose when content is AI-generated, especially in:
- Media
- Education
- Research
- Marketing
3.2 Ethical Data Collection
Use datasets that are
- Licensed
- Open
- Permission-based
Avoid scraping private or copyrighted content without consent.
3.3 Bias Testing and Model Audits
Regularly test outputs for:
- Discrimination
- Representation errors
- Harmful patterns
Human oversight remains essential.
3.4 Implement Safety Guardrails
Examples include
- Filters for harmful content
- Digital watermarks for generative media
- Identity verification systems
3.5 Promote Human-AI Collaboration
Use AI for
- Assisting creativity, not replacing it
- Enhancing efficiency, not removing jobs
- Supporting education and skill-building

How Can You Learn Neural Networks for Generative AI in 2026?
Generative AI is one of the most in-demand skills today, and learning it can unlock opportunities in software development, research, design, product management, and more. This section provides a clear, actionable learning path for beginners, students, and professionals.
1. What Is the Best Learning Path for Students and Beginners?
If you’re new to generative AI, follow this structured roadmap:
Step 1: Learn the Basics of AI and Machine Learning
- What is a neural network?
- How do models learn?
- What is training data?
Recommended beginners’ topics:
- Linear regression
- Classification
- Loss functions
- Optimizers
- Basic Python
Step 2: Understand Neural Network Architectures
Study
- Feedforward networks
- CNNs
- RNNs, LSTMs, GRUs
- Transformers
Step 3: Start Building Simple Models
Use frameworks like
- TensorFlow
- PyTorch
- Keras
Projects
- Digit recognition using MNIST
- Simple text generator
- Basic autoencoder
Step 4: Learn GANs, VAEs, and Sequence Models
Understand
- Generator–discriminator training
- Latent spaces
- Reconstruction loss
- Sequence modeling
Step 5: Work on Generative AI Projects
Examples
- AI image generator
- Music creator using RNNs
- Face interpolation using VAEs
- Text generator for short stories
Step 6: Build a Portfolio
Include
- Colab notebooks
- GitHub repos
- Sample outputs (images, audio, text)
A portfolio is essential for demonstrating your skills to employers.
2. How Should Working Professionals Upskill Quickly?
Professionals may not have time for long academic paths. Here’s an efficient plan:
2.1 Learn by Doing
Pick a generative AI tool and start experimenting:
- ChatGPT-like tools
- Midjourney / Stable Diffusion
- RunwayML
- PyTorch Hub pretrained models
2.2 Focus on Practical Applications
Examples
- Generate product ads
- Automate reports
- Build chatbots
- Improve customer experiences
- Create synthetic datasets for testing
2.3 Add Essential Coding Skills (if needed)
You don’t need to be a full-time programmer.
Focus on
- Python
- NumPy
- PyTorch basics
2.4 Take Micro-Certifications
Short, focused courses
- Deep learning
- GANs
- Transformers
- Applied AI ethics
2.5 Learn to Collaborate With AI Tools
In 2026, effectiveness depends not on replacing humans but on working with generative AI efficiently.
3. What Tools and Frameworks Should You Use?
Here’s a summary of the most useful tools for learning generative AI:
Tool / Framework | Best Use Case | Skill Level | Notes |
PyTorch | Custom neural networks, research | Intermediate | Most popular in 2026 |
TensorFlow / Keras | Beginner models, production | Beginner–Intermediate | Easy syntax, great documentation |
Hugging Face Transformers | Text and multimodal generation | Intermediate | Pretrained models for fast results |
Stable Diffusion / Automatic1111 | Image generation | Beginner | No coding required |
RunwayML | Video and creative generation | Beginner | Drag-and-drop interface |
Google Colab | Training models in the cloud | Beginner | Free GPU access |
Fast.ai | Simplified deep learning | Beginner | Project-focused learning |
Choose tools based on your goals, not trends.
4. Which Free and Paid Learning Resources Do Experts Recommend?
Here are curated learning resources from trustworthy organizations:
Free Resources
- Fast.ai – Practical Deep Learning for Coders
- Google Machine Learning Crash Course
- MIT OpenCourseWare – Deep Learning (mit.edu)
- DeepLearning.AI YouTube tutorials
- PyTorch official documentation
Paid Certifications
- Coursera – Deep Learning Specialization (Andrew Ng)
- Udacity – Machine Learning Engineer NanoDegree
- DeepLearning.AI GANs Specialization
- O’Reilly learning platform
- edX – HarvardX AI courses
- Brolly AI — Generative AI Training Program, a hands-on course covering neural networks, GANs, VAEs, transformers, and real applied projects designed for both beginners and professionals.
High-Value Books (Beginner to Expert)
- Deep Learning — Goodfellow, Bengio, Courville
- Hands-On Machine Learning — Aurélien Géron
- Grokking Deep Learning — Andrew Trask
These resources give you both theory and practical experience.
What Generative AI Trends Should You Watch in 2026 and Beyond?
Generative AI is evolving rapidly, and as we move into 2026, several trends are shaping its future. These trends impact developers, businesses, educators, and everyday users — and understanding them will help you stay ahead.
1. What Technical Innovations Will Shape the Future of Generative AI?
1.1 Multimodal AI Becomes Standard
Models are no longer limited to text or images — they now generate multiple formats simultaneously
- Text → Image
- Image → Video
- Audio → Animation
- Video → Text explanations
Large multimodal models (LMMs) integrate images, audio, code, and 3D content in one system.
1.2 Smaller and More Efficient Models
We are seeing a shift from massive, resource-heavy models to compressed, distilled, and edge-deployable networks.
Techniques like
- Quantization
- Distillation
- Low-rank adaptation (LoRA)
allow models to run on laptops, phones, and even IoT devices.
1.3 Diffusion + GAN Hybrid Architectures
GANs are sharp, diffusion models are stable — combining them:
- Improves image quality
- Speeds up generation
- Reduces artifacts
2026 models increasingly use hybrid pipelines.
1.4 Real-Time Generative Video
Advancements in GPU acceleration allow:
- Live scene generation
- Real-time AI avatars
- Instant video editing
This is transforming film production and video content creation.
1.5 Neural Rendering for 3D Environments
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) and 3D GANs enable:
- Virtual worlds for games
- Digital twins for simulation
- Photorealistic AR/VR environments
3D generative AI is one of the fastest-growing areas.
2 How Will Industry Adoption of Generative AI Evolve?
2.1 Enterprises Will Build Their Own Generative Models
Instead of relying on public models, companies are now training:
- Private models for security
- Industry-specific models
- Internal assistants for employees
Businesses want full control over data and output quality.
2.2 AI Becomes a Standard Tool in Creative Workflows
Creative professionals now use AI for
- Storyboarding
- Music composition
- 3D asset creation
- Marketing and branding
AI is becoming a co-creator, not a replacement.
2.3 AI Regulations Strengthen Globally
Countries and organizations are introducing rules around:
- Deepfake labeling
- Data consent
- Ethical AI disclosures
- Safety testing for large models
Expect transparency and traceability requirements to increase.
2.4 Surge in AI Workforce Demand
By 2026, companies will hire aggressively for roles like:
- Generative AI engineer
- AI ethics officer
- AI product designer
- Prompt engineer
- Applied AI researcher
AI skills are becoming essential across fields.
3. What Skills Will Be Most Valuable Moving Forward?
To stay competitive in AI-driven industries, here are the most valuable skills to master:
Technical Skills
- Neural network fundamentals
- GANs, VAEs, RNNs, Transformers
- Python, PyTorch, TensorFlow
- Data curation and preprocessing
- Generative model fine-tuning (LoRA, PEFT)
Creativity + AI Collaboration
You’ll need to know
- How to prompt models effectively
- How to evaluate and refine AI outputs
- How to combine multiple AI tools into a workflow
Ethical & Responsible AI Understanding
Companies want professionals who can use AI safely, including:
- Bias detection
- Risk assessment
- Compliance awareness
- Privacy protection
Problem Solving With AI
The most valuable workers in 2026 can identify:
- Where AI fits
- How to integrate it
- How to measure its impact
This blend of technical + creative + strategic skills defines future AI careers.
Conclusion
As we enter 2026, generative AI powered by neural networks is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s an everyday reality reshaping how we learn, work, create, and solve problems. Whether you’re a student, a working professional, or a non-technical learner, understanding neural networks for generative AI opens the door to incredible opportunities.
Let’s review the key insights you’ve learned in this guide.
1. What Did You Learn About Generative AI?
You now understand
- What generative AI is and how it works
- Why neural networks are the engines behind AI creativity
- Key architectures like GANs, VAEs, and RNNs
- Important algorithms such as backpropagation, adversarial training, and variational inference
- Real-world applications across industries in 2026
- Ethical risks and how to use generative AI responsibly
- How to begin learning or upskilling in this field
This knowledge gives you a solid foundation for both academic growth and professional advancement.
2. Why Are Neural Networks Essential to the Future of AI?
Neural networks allow generative models to
- Learn patterns in massive datasets
- Understand structures like language and vision
- Create realistic and innovative outputs
- Adapt to new tasks without complete retraining
- Power multimodal systems that combine text, images, audio, and video
Whether it’s autonomous vehicles, personalized education, drug discovery, or creative content, neural networks form the brain of the system.
3. How Can You Move Forward From Here? (Action Steps)
Here’s your practical roadmap:
Step 1: Start Learning the Basics
- Python
- Deep learning fundamentals
- How neural networks work
Step 2: Explore Generative Models
- Build a simple VAE
- Experiment with a GAN
- Generate text using an RNN or Transformer
Step 3: Work on Small Projects
Ideas
- AI-based art generator
- Music composition model
- Simple chatbot
- Face interpolation tool
Projects help you understand concepts better than theory alone.
Step 4: Create a Portfolio
Show your skills using
- GitHub repositories
- Google Colab notebooks
- Sample outputs (images, audio, code)
Step 5: Stay Updated With AI Trends
Follow
- Research papers
- Industry reports
- AI regulatory updates
- Open-source communities
Staying current is essential in a field evolving this quickly.
4. Final Motivation: The Future Belongs to Those Who Learn With AI, Not Against It
Generative AI isn’t meant to replace human creativity—it’s designed to enhance it.
In 2026 and beyond
- Students who learn with AI learn faster
- Professionals who adopt AI tools become more productive
- Creators who collaborate with AI unlock new levels of innovation
- Organizations that integrate AI thoughtfully gain a competitive edge
You now have the knowledge and roadmap to join this transformation.
Start small, stay curious, and keep building—your future in generative AI begins today.
FAQs
Neural networks learn patterns from data and generate new outputs such as text, images, audio, or video.
It depends on your goal:
- GANs → realistic images
- VAEs → structured latent spaces
- RNNs → sequential data
- Transformers → large-scale text & multimodal generation
GANs produce sharper images, while VAEs produce smoother and more controlled outputs. Neither is universally better.
RNNs remember previous inputs, making them ideal for sequences like text, speech, and music.
Yes. Tools like RunwayML, Stable Diffusion GUIs, and AI art platforms require no coding. Coding becomes useful later for custom models.
Beginners can learn basic models in 2–3 months; reaching intermediate skill takes 6–12 months with practice.
They need many examples to learn patterns, reduce bias, and generate realistic outputs.
It creates new combinations of learned patterns. Outputs aren’t exact copies, but they are influenced by training data.
Major risks include deepfakes, misinformation, bias, privacy issues, and copyright violations.
Healthcare, education, entertainment, cybersecurity, retail, finance, and manufacturing lead adoption.
Basic math helps (algebra, probability), but deep math is not required for beginners.
Latent space is a compressed representation of data where features are stored. Models generate new content by sampling from it.
Mode collapse happens when the generator produces limited output variations because it learns to fool the discriminator with a narrow set of patterns.
Diffusion models often outperform GANs in stability and quality, but GANs remain valuable for real-time generation and certain image tasks.
- Training is when a model learns from data.
- Inference is when it generates or predicts using what it has learned.
Small models: yes.
Large models like GANs or Transformers typically require GPUs or cloud computing.
Python is essential. Libraries like PyTorch, TensorFlow, and Hugging Face simplify model creation.
By ensuring transparency, avoiding biased data, watermarking AI-generated media, respecting copyright, and prioritizing human oversight.
- Stable Diffusion
- Midjourney
- RunwayML
- ChatGPT & multimodal LLMs
- Hugging Face models
Yes—demand is rapidly growing for roles like:
- Generative AI Engineer
- AI Researcher
- Prompt Engineer
- AI Product Designer
- Data Scientist
Generative AI skills are considered high-value across industries.
FINAL KEY TAKEAWAY: What Should You Remember About Neural Networks for Generative AI?
Generative AI is transforming industries, learning, creativity, and everyday technology — and neural networks are the driving force behind this transformation. As you move into 2026 and beyond, here’s what truly matters:
Generative AI Creates, Not Just Predicts
It learns patterns from data and generates new images, text, audio, video, 3D models, and simulations.
Neural networks make this possible by recognizing complex relationships and reproducing them creatively.
Every Neural Network Type Has a Purpose
- GANs = realism and high-quality images
- VAEs = structure, smooth latent spaces, and controlled generation
- RNNs (LSTMs, GRUs) = sequences and time-dependent data
- Transformers = large-scale text and multimodal generation
No architecture is universally best — the “right” one depends on the task.
Learning Happens Through Powerful Algorithms
Generative models learn using:
- Backpropagation
- Gradient descent
- Variational inference
- Adversarial training
- Sampling methods
- Latent space manipulation
These algorithms allow models to improve, adapt, and innovate.
Generative AI Is Transforming Every Major Industry
From education and entertainment to healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and cybersecurity, generative AI enhances:
- Creativity
- Productivity
- Personalization
- Simulation
- Automation
Neural networks bring intelligence, efficiency, and imagination to real-world applications.
Ethical and Technical Challenges Must Be Addressed
The rise of generative AI brings concerns about:
- Deepfakes
- Misinformation
- Bias
- Copyright
- Privacy
- High compute demands
Responsible AI frameworks and transparency are essential to protect users and maintain trust.
Your Path Forward Is Clear
Whether you’re a student, professional, or non-technical learner:
- Start with the basics of neural networks
- Learn about GANs, VAEs, RNNs, and Transformers
- Work on small but meaningful projects
- Build a portfolio
- Stay updated with trends like multimodal AI and 3D generation
You don’t need to master everything at once — just take one step at a time.
The Future Belongs to Those Who Collaborate With AI
Human creativity + neural network intelligence = exponential potential.
Generative AI won’t replace you — but someone using generative AI might.
So embrace the technology, experiment boldly, and continue learning.
Your journey into the future of AI starts now.
