Prompt Engineering Roadmap for 2025: From Beginner to Pro
Why Prompt Engineering Matters in 2025
What Is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is the science — and art — of communicating effectively with AI models like ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, or Llama 3.
In simple words, it’s about writing instructions (“prompts”) that guide these models to produce accurate, creative, or useful outputs.
Think of it like teaching AI how to think — not by coding, but through structured conversation.
A “prompt” could be as short as:
“Write a poem about sustainability.”
Or as complex as
“Act as a financial advisor. Summarize this report in bullet points, highlight three risks, and suggest two data-backed investment strategies.”
Why it matters
- Every generative AI tool depends on prompts — whether for text, image, or code.
- 2025 is seeing a shift from model-building to model-using. Many companies now need prompt engineers more than machine-learning engineers.
- AI adoption in business, education, design, and software means people who can instruct AI effectively have a huge advantage.
According to Gartner’s 2025 AI Skills Report, over 40% of new AI-related roles involve prompt design, evaluation, or orchestration.
Who Should Learn Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering isn’t just for data scientists. In 2025, it’s a must-have skill for
- Students exploring AI/ML or computer science.
- Professionals in marketing, design, software, or analytics using AI tools.
- Educators and trainers are leveraging LLMs to build learning assistants.
- Non-tech learners or freelancers who want to use ChatGPT or Midjourney effectively.
If you’ve ever used ChatGPT or DALL·E, you’ve already done prompt engineering (just not systematically yet).
Job Market and Career Outlook
Global Snapshot (2025)
Region | Average Salary (USD/year) | Growth Trend | Common Titles |
USA | $120K – $160K | Rapid | Prompt Engineer, AI Instruction Designer |
Europe | €80K – €130K | Steady | Generative AI Specialist |
India | ₹12 – 25 LPA | Fast-rising | LLM Engineer, AI Workflow Designer |
APAC | $90K – $130K | Growing | AI Operations Analyst |
(Source: LinkedIn Talent Insights 2025, OpenAI Job Trends Report)
Insight: Companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, Google DeepMind, and Accenture are actively hiring prompt engineers to fine-tune enterprise workflows and train AI assistants.
Key Terms to Understand Before You Start
Term | Meaning | Example |
Prompt | The instruction given to an AI model. | “Summarize this article in 5 bullet points.” |
LLM (Large Language Model) | The AI system is trained on massive text datasets to understand and generate language. | GPT-4, Claude 3, Gemini 1.5 |
Zero-Shot Prompting | Directly prompting the model to solve a task without prior examples. | “Translate this sentence into French.” |
Few-Shot Prompting | Giving the AI some sample inputs and answers so it knows how to behave. | “Here are 3 Q&A examples — now answer the 4th.” |
Fine-Tuning | Retraining a model on specific data for specialized tasks. | A company fine-tunes GPT for internal support chats. |
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) | Combining AI with a knowledge base for factual accuracy. | Chatbot retrieves company FAQs before answering. |
Why 2025 Is the Perfect Time to Learn Prompt Engineering
- LLMs are everywhere: from Gmail Smart Compose to Notion AI to customer-support bots.
- Low entry barrier: you don’t need to code — just think logically and express clearly.
- High-paying, creative roles available across industries.
- Tools are more accessible: OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google Cloud all offer playgrounds for free experimentation.
- Future-proof skill: as models evolve, prompt engineers will guide them, test them, and integrate them responsibly.
Quick takeaway:
Prompt engineering isn’t a passing trend — it’s a core communication skill for the AI age.
In the next section, we’ll break down the types of prompts you’ll use every day — and how to master them.
Types of Prompts — The Building Blocks of Effective Prompting
Before you dive into prompt frameworks and advanced tools, you need to understand the different kinds of prompts and how they shape an AI model’s response.
Think of this as learning the grammar of talking to AI — once you master it, you can control tone, depth, creativity, and accuracy with ease.
What Are the Main Types of Prompts?
Prompting isn’t one-size-fits-all. Depending on your goal — explanation, reasoning, creativity, or coding — you’ll use a different structure.
Here are the main categories every prompt engineer should know in 2025:
Prompt Type | Description | Best For | Example |
Instructional Prompts | Directly tell the model what to do, step-by-step. | Tasks, structured outputs. | “List 5 tips for learning Python.” |
Socratic Prompts | Ask guiding questions to get reasoning or reflection. | Learning, analysis, brainstorming. | “Why do transformers outperform RNNs in NLP?” |
Priming Prompts | Give background or context before asking a question. | Maintaining consistency or persona. | “You’re an AI ethics expert. Explain the bias issue in LLMs.” |
Example-Based Prompts (Few-Shot) | Provide examples to teach format or logic. | Pattern learning and accuracy. | “Q: 2+2 = 4; Q: 3+3 = 6; Q: 5+5 = ?” |
Mixed or Hybrid Prompts | Combine instructions, examples, and roles. | Complex workflows, coding, or content generation. | “Act as a tech writer. Here’s a sample; now create one for LLMs.” |
Multimodal Prompts (New 2025) | Use text + images + code for richer input. | Design, research, and visual AI tasks. | Upload image + ask: “Describe this scene in 100 words.” |
Instructional Prompts: Clarity Is Power
Instructional prompts form the foundation of effective communication with AI.
How they work
You clearly define your goal, format, and sometimes tone.
Formula
Action + Topic + Context + Constraints (optional)
Example
“Summarize this article in 3 sentences using simple language suitable for high-school students.”
Pro Tips
- Start with verbs: Write, Summarize, Explain, Design, Compare.
- Specify the output format (list, paragraph, table).
- Add boundaries: “under 100 words,” “in formal tone.”
When to use
- Summaries, reports, data extraction, and code explanations.
Socratic Prompts: Teaching the AI to Think
This technique uses guided questioning — you don’t give direct instructions but lead the AI to reason through the topic.
Example
“What happens if a model is over-fit? How can regularization help prevent it?”
This works well for
- Education and tutoring bots.
- Deep analysis or reasoning-based discussions.
- AI-assisted learning systems (edtech, training).
Pro Tips
- Ask “why,” “how,” and “what if” questions.
- Chain questions logically to help the AI refine its reasoning.
Priming Prompts: Set the Stage
Priming means giving the model a role or context before the main question.
It influences how the AI interprets the prompt.
Example
“You are a career coach. Suggest 3 ways for a data analyst to transition into prompt engineering.”
Benefits
- Maintains tone and personality throughout the conversation.
- Reduces inconsistency in long chats.
Advanced Use (2025 Trend)
Priming is now part of “agentic prompting”, where AI models retain roles or goals across multiple messages — used in frameworks like LangChain Agents and OpenAI Assistants API.
Example-Based Prompts: Teach by Showing
Few-shot prompting demonstrates a pattern through examples, so the AI learns what you expect.
Structure
Input → Output (Example 1)
Input → Output (Example 2)
Input → Output (Your Turn)
Example
Q: Translate “Hello” to Spanish → Hola
Q: Translate “Good Morning” to Spanish → Buenos Días
Q: Translate “Thank You” to Spanish →?
Why it matters
- Increases accuracy in tasks requiring consistency.
- Reduces hallucinations by grounding responses.
- Especially useful in code generation, translation, and summarization.
Mixed or Hybrid Prompts: Real-World Complexity
Most production-level prompts today are hybrids.
You might combine priming + examples + instructions to build a single powerful workflow.
Example
“You are an AI writing tutor. Analyze the student essay below, grade it A–F, give 3 strengths, 3 improvements, and rewrite one paragraph in formal English.”
Why it works
- Maintains persona.
- Produces structured, high-quality results.
- Perfect for multi-step automation in chatbots, agents, or education apps.
Multimodal Prompts: The Future of AI Interaction
2025 is the year of multimodal prompting — combining text, images, audio, and code.
With models like GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5 Pro, and Claude 3 Opus, you can now feed images or diagrams into the prompt for deeper reasoning.
Use Cases
- Describe, caption, or analyze images.
- Generate designs or visual instructions.
- Interpret charts and graphs.
Example
Upload an image of a dashboard → ask:
“What are the top 3 insights from this chart?”
Bonus: Choosing the Right Prompt Type
Goal | Best Prompt Type | Example |
Learn a concept | Socratic | “Why are embeddings crucial in NLP?” |
Generate content | Instructional / Mixed | “Write a LinkedIn post about AI ethics.” |
Analyze data or text | Priming + Example-Based | “Act as a data analyst. Given the dataset summary, find anomalies.” |
Brainstorm ideas | Socratic / Mixed | “List 5 creative startup ideas for healthcare AI.” |
Code generation | Few-Shot / Instructional | “Here are examples of SQL queries. Write one for total revenue per region.” |
Design tasks | Multimodal / Priming | “Here’s a wireframe. Suggest UI improvements.” |
Actionable Tips
- Keep prompts short but precise (under 100 words for most tasks).
- Iterate — tweak one variable at a time to see the effect changes.
- Always include context, constraints, and desired output format.
- Save your best prompts — build a “Prompt Library” or portfolio.
Quick Summary
- Prompts come in several flavors — choose based on your goal.
- Start simple (instructional) and evolve to complex (hybrid, multimodal).
- 2025 introduces agentic & multimodal prompting, making roles and context retention vital.
Core Skills & Foundations You Need to Become a Prompt Engineer
Prompt engineering is more than typing clever questions into ChatGPT.
It’s a blend of technical understanding, linguistic precision, and creative problem-solving.
Think of it like learning to communicate fluently in AI’s language.
The better you understand how models “think,” the better you can make them work for you.
1. Foundation Tech Skills: Learn the Language of AI
Even if you’re not a programmer, getting comfortable with a few fundamentals will 10× your prompt quality.
a. Learn Basic NLP and Machine Learning Concepts
Before you write prompts, it helps to know how models interpret words.
- What is tokenization?
→ The model breaks text into chunks (“tokens”) to process meaning. - What are embeddings?
→ Vectors that represent the meaning of words. - What’s a transformer model?
→ The core architecture behind GPT, Gemini, and Claude — it “pays attention” to relationships between words.
Learn from
- Coursera – Natural Language Processing Specialization (deeplearning.ai)
- Stanford NLP Course Notes (cs224n.stanford.edu)
Goal: Understand what happens “under the hood” when you write a prompt.
b. Learn Basic Python (and a Little Code Logic)
You don’t have to become a full-stack developer — but Python gives you control.
You’ll use it to interact with APIs, automate prompt testing, and fine-tune small models.
Learn
- Variables, functions, and loops
- Using APIs (requests, OpenAI, langchain)
- Reading/writing data (JSON, CSV)
Example
import openai
prompt = “Summarize the benefits of multimodal AI in 2025.”
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(model=”gpt-4o”, messages=[{“role”: “user”, “content”: prompt}])
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
Free practice
- W3Schools Python Basics
- Google Colab for online notebooks
c. Explore NLP Libraries & Frameworks
Once you’re comfortable with Python, explore the key tools that power prompt workflows.
Tool | Purpose | 2025 Usage |
LangChain | Build multi-step AI pipelines with memory and context. | Used in production chatbots and agents. |
LlamaIndex (GPT Index) | Connect LLMs with external knowledge bases. | Useful for RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation). |
OpenAI API / Gemini API | Directly test and automate prompt responses. | Core for developers and analysts. |
Hugging Face Transformers | Train and fine-tune smaller LLMs. | Advanced use for AI researchers. |
Pro Tip: Start with OpenAI’s Playground → then automate via LangChain → then fine-tune with Hugging Face.
2. Prompt Design & Communication Skills
Prompt engineering is half-tech, half-language.
You must think like a teacher and talk like a designer.
a. Clarity and Specificity
AI models are like students — vague questions confuse them.
Don’t
“Tell me about AI.”
Do
“Explain three key trends in AI in 2025 — focus on education, health, and business — in bullet points.”
b. Context and Constraints
Provide background (what the AI should know) and limits (word count, tone, style).
Example
“You are a resume expert. Rewrite this resume summary in a confident tone under 80 words.”
c. Iteration Is Key
Don’t expect perfect results on the first try.
Prompt engineering is experimental — tweak, test, and compare.
Technique
Change only one variable per iteration (like an experiment).
Use a “prompt log” — track what works best.
3. Soft Skills Every Prompt Engineer Needs
a. Analytical Thinking
You must interpret vague requests and turn them into structured AI instructions.
Example: turning “make this better” → “rewrite this email in a friendly yet professional tone for a sales audience.”
b. Creativity
Prompt engineering often feels like brainstorming with AI.
You’ll explore multiple tones, formats, and perspectives.
Try:
“Act as a 1950s journalist writing about AI ethics in 2025.”
You’ll be amazed by the creative angles it produces.
c. Domain Knowledge
Specializing pays. Prompt engineers who understand finance, healthcare, education, or marketing build better task-specific prompts.
4. Ethics, Bias, and Responsible AI
2025 prompt engineers must think ethically.
AI can reflect or amplify human bias if prompts are careless.
Key practices
- Avoid loaded or discriminatory phrasing.
- Double-check facts and sources.
- Label AI-generated content transparently.
- Use AI fairness guidelines from OECD.AI and Partnership on AI.
Example
Ethical prompt:
“Write a gender-neutral job description for a project manager role.”
5. “Month-1 Learning Checklist” — Quick Start Plan
Week | Goal | What to Learn | Tools |
1 | Understand LLM Basics | Watch short videos on transformers & NLP. | YouTube: 3Blue1Brown, DeepLearning.ai |
2 | Learn Python Syntax | Practice small programs daily. | Google Colab, W3Schools |
3 | Try Your First Prompts | Experiment in ChatGPT or Gemini Playground. | OpenAI Playground |
4 | Create a Prompt Log | Record 10 best prompts & results. | Notion, Excel, or PromptLayer |
End of Month 1 Objective
You can explain how LLMs work, write structured prompts, and test results systematically.
Summary
By mastering these foundations, you’ll
- Understand how AI models think and why prompts work.
- Communicate ideas clearly and systematically.
- Develop the analytical and creative skills to solve real-world problems with AI.

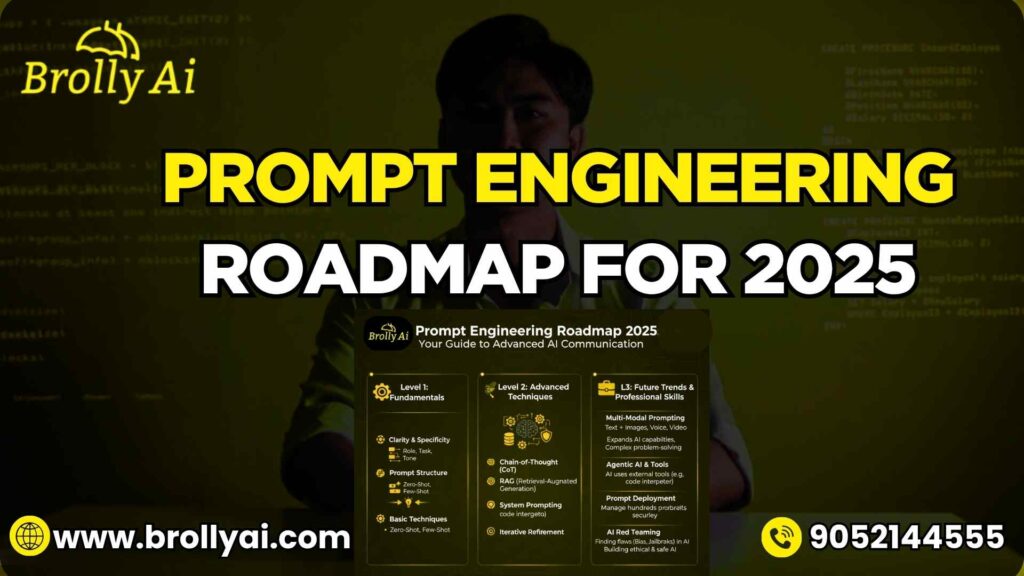
The 12-Month Prompt Engineering Roadmap (Beginner → Intermediate → Professional)
Whether you’re starting from scratch or already tech-savvy, this roadmap will guide you through what to learn, when to learn it, and how to practice it.
Each phase includes learning goals, free tools, and actionable projects to build your AI prompt portfolio.
0–3 Months: Build Strong Fundamentals
Goals
- Understand how LLMs work
- Learn Python basics
- Master simple and few-shot prompts
- Create your first small projects
What to Learn
- NLP & transformer basics (how AI understands language)
- Python fundamentals (functions, loops, APIs)
- Prompt structures: instruction, few-shot, role, and context-based
- How to evaluate and improve prompt responses
Tools to Explore
- ChatGPT Playground or Gemini Studio
- LangChain Hub (for visual prompt flow building)
- PromptLayer (track and version prompts)
Mini-Projects
- Create a prompt-based chatbot that answers FAQs for your college or company.
- Build a text summarizer using OpenAI API and Python.
- Experiment with AI content rewriting — from casual to professional tone.
Skills Focus | Output | Tools |
NLP Basics | Blog or notebook notes | YouTube, Coursera |
Prompt Practice | Prompt Library | ChatGPT Playground |
Project | Simple chatbot | Python + OpenAI API |
End-Goal: You can confidently write clear, structured prompts and understand how models interpret them.
3–6 Months: Transition from User to Builder
Goals
- Experiment with intermediate prompting techniques
- Learn prompt chaining and orchestration
- Start using APIs and frameworks like LangChain
- Work on structured, multi-step projects
What to Learn
- Few-shot prompting (teaching by examples)
- Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting for reasoning tasks
- Introduction to LangChain and LlamaIndex
- Working with RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) setups
- Ethics and bias detection in AI outputs
Tools to Explore
- LangChain, LlamaIndex, OpenAI API, Anthropic API, Hugging Face Hub
- Prompt Engineering Notebooks (Google Colab)
- Pinecone or ChromaDB for vector storage (RAG)
Mini-Projects
- Build an AI Resume Reviewer (upload a PDF → get personalized feedback).
- Create a multi-step email assistant using LangChain.
- Design a domain-specific prompt library (e.g., for educators or marketers).
Skills Focus | Output | Tools |
Prompt Chaining | Multi-step app | LangChain |
RAG Basics | Search-enhanced bot | LlamaIndex |
Ethics in AI | Guidelines doc | Notion, Markdown |
End-Goal: You can build small LLM applications using prompt chaining and understand context-aware AI responses.
6–12 Months: Become a Professional Prompt Engineer
Goals
- Master advanced techniques and fine-tune
- Learn multimodal and agentic prompting
- Build a public portfolio and contribute to open source
- Prepare for certifications or freelancing
What to Learn
- Advanced Prompt Patterns: Role-play, self-consistency, tree-of-thought reasoning
- Prompt Evaluation Metrics: Coherence, factuality, fluency
- Prompt Testing Frameworks: Guardrails AI, PromptSource
- Fine-tuning LLMs: adapting open-source models like Mistral 7B
- Multi-modal prompting: combining text + image + code
- Responsible Prompt Design: using ethical AI frameworks
Tools to Explore
- LangSmith, Weights & Biases, Guardrails AI
- Hugging Face Transformers, OpenAI Finetuning Dashboard
- Midjourney, GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5 Pro (for multimodal tasks)
Capstone Projects
- AI Teaching Assistant: A chatbot trained on educational content to tutor students.
- Creative Content Generator: Automate content creation for blogs or marketing.
- Prompt Quality Evaluator: Build a small app that scores prompt clarity or creativity.
Skills Focus | Output | Tools |
Advanced Prompting | Complex workflows | LangChain, OpenAI API |
Fine-tuning | Custom AI model | Hugging Face |
Portfolio Building | Website + GitHub | Notion, Replit, GitHub Pages |
End-Goal: You can design, test, and deploy prompt systems that solve real-world problems — and confidently apply for prompt engineering jobs or freelance projects.
Bonus: Tailored Paths for Different Learners
Persona | Recommended Focus | Learning Strategy |
Students | Fundamentals + Portfolio Projects | Focus on Python, LangChain, and building a public prompt repo. |
Working Professionals | Applied AI in your domain | Learn automation with APIs; apply prompts to daily workflows. |
Non-Tech Learners | No-code Tools + Prompt Craft | Use ChatGPT, Notion AI, or Brolly AI to build real projects without coding. |
Summary Table: 12-Month Learning Timeline
Phase | Duration | Focus | Deliverables |
Beginner | 0–3 mo | Fundamentals + Prompt Basics | Prompt Library + Mini-Chatbot |
Intermediate | 3–6 mo | Prompt Chaining + APIs | RAG Bot + Portfolio Prompts |
Advanced | 6–12 mo | Fine-Tuning + Multimodal AI | Capstone Project + Public Portfolio |
Quick Tips for Staying Consistent
Set micro-goals — learn one new prompt type per week.
Join AI communities (Reddit r/PromptEngineering, Discord LangChain).
Read 1 research paper per month (use PapersWithCode.org).
Participate in hackathons — real practice > theory.
Keep your portfolio updated — recruiters love documented examples.
Takeaway
You don’t need a Ph.D. to become a prompt engineer.
You need discipline, curiosity, and a structured learning path.
Follow this roadmap, and in 12 months, you’ll go from experimenting with ChatGPT to building production-ready AI assistants that enhance how businesses and people work.
Tools, Frameworks & Platforms Every Prompt Engineer Should Know (2025 Edition)
If prompt engineering is the skill, tools are your instruments.
They help you design, test, automate, and evaluate prompts at scale.
2025 has brought a wave of AI orchestration frameworks, monitoring dashboards, and multimodal playgrounds — and learning how to pick the right one saves you tons of time.
1. Prompt Testing & Playground Tools
These tools let you safely experiment and visualize how your prompts behave before deploying them.
Tool | What It Does | Pros | Ideal For |
OpenAI Playground | Test GPT-4 / GPT-4o responses interactively | Free tier, real-time tuning, API preview | Beginners → Intermediate |
Gemini Studio (Google) | Multimodal prompt experiments (text + image + video) | Supports multimodal chains | Non-coders, researchers |
Anthropic Console | Claude 3 family prompt lab | Long-context testing | Professionals |
PromptLayer | Tracks and versions prompts | Great for iteration history | Teams, freelancers |
Brolly AI Prompt Builder | Visual, drag-and-drop prompt design | No-code simplicity | Marketers, educators |
Pro Tip: Keep a “Prompt Journal” — screenshot or export your best prompts to Notion or Excel for future reuse.
2. Frameworks for Building Prompt Workflows
These frameworks let you chain prompts together, connect APIs, and manage context (memory) — essential for multi-turn conversations or AI apps.
Framework | Description | Why It Matters in 2025 | Use Case Example |
LangChain | Most popular Python/JS library for prompt orchestration | Powers agents, memory, retrieval, tools | Chatbots, assistants |
LlamaIndex (GPT Index) | Interface to connect LLMs with external data | Enables Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) | Corporate knowledge bots |
DSPy (Stanford) | Declarative syntax for structured prompting | Academic & reproducible | Research, AI pipelines |
Gradio / Streamlit | Simple UI for LLM apps | Great for demos | Interactive prototypes |
Guardrails AI | Adds validation and safety checks | Prevents toxic/broken output | Enterprise deployments |
2025 Trend
LangChain + LlamaIndex now integrates multi-agent orchestration, letting multiple specialized AIs collaborate — a must-know for advanced prompt engineers.
3. Fine-Tuning & Customization Tools
When prompts alone aren’t enough, you can fine-tune models to better understand your data or tone.
Tool | Function | Use Case |
OpenAI Fine-Tuning Dashboard | Train GPT 3.5/4 on custom datasets | Corporate chatbots |
Hugging Face Transformers | Fine-tune open-source LLMs | Research / on-prem solutions |
Weights & Biases | Track training runs and metrics | Experiment management |
LoRA Adapters / PEFT Libraries | Lightweight fine-tuning methods | Cost-efficient customization |
Pro Tip: Fine-tuning ≠ Prompting — it’s the next layer after prompt optimization.
Learn to get 90 % results with prompting first.
4. Multimodal & Creative Prompting Tools
2025 is the era of multimodal AI — combining text, image, code, and sound.
Tool | Modality | Example Use |
GPT-4o (OpenAI) | Text + Image + Audio | Describe an uploaded photo or generate UI suggestions |
Gemini 1.5 Pro | Text + Vision + Code | Research assistants and slide generation |
Midjourney v7 | Image generation | Creative projects, design prototypes |
Runway ML | Video + Image editing | Short-form media and AI filmmaking |
Hugging Face Diffusers | Open-source image/text2img | Developers and artists |
Example Prompt
“Generate three infographic concepts explaining Chain-of-Thought Prompting — minimalistic style, blue-white palette.”
5. Evaluation & Prompt Quality Tools
Once you build prompts, you need to measure their effectiveness — just like A/B testing in marketing.
Tool | What It Measures | How It Helps |
PromptLayer Analytics | Accuracy/latency/cost | Identify high-performing prompts |
PromptSource (Hugging Face) | Dataset of tested prompts | Learn from community examples |
TruLens | Evaluate LLM responses with metrics | Detect hallucinations |
LangSmith (by LangChain) | Monitor chains, debug flows | Enterprise tracking |
PromptPerfect | Suggests refinements automatically | Great for optimization |
Key Tip: Track three metrics — accuracy, clarity, and cost per run.
6. AI Collaboration & Deployment Tools
When your prompts turn into apps, these tools let you deploy, scale, and collaborate.
Tool | Function | Notes |
Replit + LangChain Starter | Build web apps quickly | Great for portfolios |
Vercel / Hugging Face Spaces | Host front-ends + models | Free tiers for demos |
Streamlit Cloud | Deploy Python LLM apps easily | No DevOps required |
Notion + Zapier AI | Automate workflows using LLMs | Ideal for non-tech pros |
Comparison Table — Best Tools by Skill Level
Skill Level | Recommended Tools | Why These |
Beginner | ChatGPT Playground, PromptLayer, Gemini Studio | Simple UIs + visual experimentation |
Intermediate | LangChain, LlamaIndex, PromptPerfect | Control, chaining, optimization |
Advanced / Pro | Guardrails AI, LangSmith, Hugging Face | Enterprise-grade reliability |
7. How to Pick the Right Tool for Your Journey
Ask yourself
- Am I just learning → use playgrounds.
- Am I building workflows → use frameworks (LangChain).
- Am I deploying apps → use evaluation + deployment tools.
Your Goal | Ideal Stack (2025) |
Learn Prompting | ChatGPT + PromptLayer |
Build LLM App | LangChain + LlamaIndex + Streamlit |
Fine-Tune Model | Hugging Face + Weights & Biases |
Deploy Portfolio | Replit / Vercel + LangSmith Monitor |
2025 Trends to Watch
- Multi-Agent Prompting – multiple AI agents collaborating with different roles.
- Auto-Prompt Optimization – frameworks like DSPy that rewrite prompts automatically for better performance.
- Prompt Security and Policy – tools like Guardrails AI ensure ethical and safe generations.
- Voice and Video Prompting – GPT-4o and Gemini are integrating real-time multimodal input.
- Prompt Engineering as a Service (PEaaS) – agencies and freelancers offering “prompt stacks” to clients.
Key Takeaways
- You don’t need to learn every tool — pick 2–3 per phase.
- Focus on playgrounds → frameworks → evaluation tools in that order.
- Stay current; the best engineers in 2025 experiment weekly.
Prompt Engineering Projects & Portfolio Ideas (Build, Showcase, and Get Hired)
In the world of AI, you’re only as good as the prompts you can provide.
Your portfolio is more than a resume — it’s a living showcase of creativity, technical skill, and problem-solving ability.
Let’s break down what you can build, how to structure your projects, and how to display them to impress employers in 2025.
Why Projects Matter More Than Certificates
Certificates are great for LinkedIn, but projects show capability.
When hiring, AI teams want to see that you can
- Structure prompts logically
- Debug or refine outputs
- Apply AI in real business or creative contexts
“Prompt engineering isn’t just theory — it’s about refining through iteration, applying context, and driving real impact.”
Your portfolio = evidence that you can make AI useful.
Types of Prompt Engineering Projects (With Examples)
1. Text Generation & Summarization Tools
Project | Goal | Tools |
Smart Summarizer | Create an app that summarizes any web article or PDF in 3 bullet points. | OpenAI API + Streamlit |
AI Resume Reviewer | Analyze resumes and suggest improvements in tone, clarity, and structure. | LangChain + ChatGPT |
Personal Writing Coach | Prompt AI to improve essays or emails while maintaining the user’s voice. | GPT-4 + Guardrails AI |
Pro Tip: Focus on clarity and tone control — two major recruiter-loved prompt skills.
2. Code Generation & Debugging Projects
Project | Goal | Tools |
SQL Query Generator | Use few-shot prompts to generate SQL queries from plain text. | GPT-4 + PromptLayer |
Code Explainer Bot | AI explains code logic line-by-line. | LangChain + Python |
Bug Fix Assistant | Chatbot identifies and corrects syntax errors. | OpenAI API + Guardrails AI |
These show technical reasoning and precision — great for engineers transitioning to AI roles.
3. Education & Learning Tools
Project | Goal | Tools |
AI Study Partner | Personalized tutor that answers questions using RAG with textbook PDFs. | LlamaIndex + GPT-4 |
Quiz Generator | Converts lecture notes into multiple-choice quizzes. | LangChain + Streamlit |
Socratic Tutor | Uses Socratic prompting to guide students through problem-solving. | Claude 3 + PromptLayer |
Why it matters: EdTech startups and universities are hiring prompt engineers for adaptive learning systems.
4. Creative and Multimodal Projects
Project | Goal | Tools |
Story-to-Image Pipeline | Convert story text → storyboard images using GPT-4o + Midjourney. | GPT-4o + Midjourney |
Headline Stylist | AI rewrites article titles in 5 different tones (formal, witty, emotional). | Gemini 1.5 Pro |
AI Video Scriptwriter | Generate video scripts and visuals for YouTube creators. | Runway ML + OpenAI |
Showcase Tip: Include your prompts + outputs side by side — recruiters love to see your “thinking process.”
5. Business & Automation Projects
Project | Goal | Tools |
Email Response Assistant | Reads incoming emails and drafts professional replies. | GPT-4 + Zapier |
Customer Support Bot | Context-aware chatbot trained on FAQs. | LangChain + LlamaIndex |
Market Research Analyzer | AI that summarizes reports and extracts trends. | OpenAI API + Python |
Why it matters: These show ROI-driven applications — perfect for enterprise AI or consulting roles.
Bonus: 5 “Weekend Projects” to Practice Prompt Craft
- Create a Prompt Library with 10+ structured examples (marketing, education, coding, research).
- Design a Prompt Improvement Log — show how you optimized a bad prompt into a great one.
- Make a Prompt Case Study (Before → After results).
- Build a Prompt Playground Notebook in Google Colab for others to try your best prompts.
- Publish a mini website with your favorite 5 projects using Notion, Replit, or GitHub Pages.
How to Build a Winning Prompt Portfolio
Structure It Like This
- Introduction Section — Who you are + why you love working with AI.
- Prompt Gallery — Screenshots, examples, and notes for each project.
- Technical Stack — Tools and frameworks you’ve used (LangChain, GPT-4, Hugging Face, etc.).
- Case Studies — Real examples showing prompt iterations and improvements.
- Links & Contact Info — GitHub, LinkedIn, or a Notion public page.
Pro Example
Notion Portfolio Example Template (free to duplicate)
How Recruiters Evaluate Prompt Portfolios
What They Look For | Why It Matters |
Clarity of Prompts | Shows communication skills |
Variety of Tasks | Demonstrates adaptability |
Prompt Testing Logs | Evidence of experimentation |
Project Documentation | Reflects professionalism |
Ethical Awareness | Ensures safe, inclusive outputs |
Extra Tip: Add “prompt notes” — explain why a certain structure worked.
That reflection shows mastery, not just usage.
Key Takeaway
You don’t need 50 projects — you need 5 great ones that demonstrate your creativity, structure, and understanding of AI behavior.
“Show me how you think, not just what you built — that’s what makes you a great prompt engineer.”

Advanced Techniques & Emerging Trends in Prompt Engineering (2025 and Beyond)
Prompt engineering is evolving rapidly.
What worked in 2023 (simple few-shot prompts) is being replaced in 2025 by multi-agent systems, chain-of-thought prompting, and multimodal orchestration.
To stay relevant, you must understand how these next-gen techniques work — and where to apply them.
1. Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Prompting
What It Is
Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting helps AI “show its work.”
Instead of giving an immediate answer, the model is guided to reason step-by-step.
Example
“What’s 27 × 14?”
“Let’s solve this step by step. 27 × 10 = 270, 27 × 4 = 108. Add 270 + 108 = 378.”
Why It Matters
- Improves accuracy in reasoning and logic tasks.
- Reduces hallucinations (AI making up facts).
- Makes outputs easier to evaluate or debug.
Use Cases
- Math and coding explanations
- Scientific problem-solving
- Legal reasoning and data analysis
Pro Tip: Combine CoT with a few-shot examples for best results.
2. Tree-of-Thought (ToT) Prompting
An evolution of CoT, Tree-of-Thought prompting explores multiple reasoning paths, then selects the best one.
Think of it like brainstorming — the AI generates several reasoning branches and picks the most logical conclusion.
Example Prompt
“List three possible ways to improve user retention. Analyze pros and cons of each, then choose the best option.”
Why It Works
- Encourages creative exploration.
- Useful for decision-making, planning, and strategy tasks.
Framework Support: LangChain’s “Self-Consistency” module and OpenAI’s “function calling” enable Tree-of-Thought workflows.
3. Self-Consistency and Reflection Prompting
In 2025, top AI systems now use reflection prompts — meta-prompts that ask the model to review or critique its own answer.
Example
“You just answered this question. Review your reasoning for errors and provide a refined version.”
This mirrors human problem-solving — draft → reflect → improve.
Use Cases
- Writing refinement
- AI moderation and safety checks
- Research synthesis
Bonus: You can chain reflection with CoT to create “AI tutors” that self-improve over time.
4. Role-Playing & Persona-Based Prompts
Setting context through roles or personas helps AI adopt expertise and tone.
Examples
- “Act as a cybersecurity analyst. Explain the top 3 data privacy risks in 2025.”
- “You’re a UX designer. Review this landing page copy for clarity and flow.”
Why It Works
- Improves contextual relevance.
- Keeps outputs consistent in long sessions.
- Useful for chatbots, education assistants, and corporate AI personas.
Real-World Application
Enterprise AIs like Salesforce Einstein and HubSpot AI now rely on persona-based prompting for tailored responses.
5. Multimodal Prompting (Text + Image + Audio + Video)
In 2025, AI isn’t just text-based.
Models like GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5, and Claude 3 Opus now handle multiple inputs and outputs — text, image, sound, and code.
Example Use Cases
Type | Example Prompt | Output |
Text + Image | “Analyze this chart and summarize key insights.” | 3-line data summary |
Text + Audio | “Transcribe and summarize this podcast.” | Blog-style summary |
Text + Code | “Here’s a Python script. Suggest 3 performance improvements.” | Annotated code |
Image + Text | “Write a polished caption for this photo that sounds professional.” | Marketing caption |
Why It Matters
- Enables richer, human-like interactions.
- Expands prompt engineering to UX, design, and accessibility.
Emerging Roles: “Multimodal Prompt Architect” and “AI Content Designer.”
6. Prompt Orchestration & Agentic AI Workflows
The biggest 2025 innovation is AI agents — autonomous systems that chain multiple prompts and tools to complete tasks.
Example
Instead of one prompt, you build a workflow like:
1 User prompt → 2 Research agent → 3 Summarizer agent → 4 Writer agent → 5 Editor agent
These multi-agent chains can collaborate, verify results, and even retry when confidence is low.
Popular Frameworks
- LangChain Agents
- AutoGPT & BabyAGI
- CrewAI (new 2025 open-source agent framework)
Use Case
Building autonomous assistants for marketing, HR, or data analysis that “think” across multiple steps.
7. Ethical and Responsible Prompting
As power grows, so does responsibility.
Ethics in prompting isn’t optional — it’s part of every professional’s workflow.
Key Ethical Practices
- Avoid bias amplification (e.g., gendered prompts).
- Disclose AI-generated content transparently.
- Avoid misleading or manipulative phrasing.
- Use guardrails or content filters for sensitive topics.
Resources
- AI Ethics Guidelines by UNESCO
- Partnership on AI Best Practices
Pro Tip: Add an “Ethical Review Step” to every prompt workflow.
Ask: Could this output harm, mislead, or misrepresent anyone?
8. Future Trends to Watch (2025–2026)
Trend | What It Means | Impact |
Auto-Prompt Optimization | AI models improve their own prompts. | Increases efficiency & reduces human tweaking. |
Prompt Compiler Tools | Convert natural language into optimized “prompt code.” | Makes workflows modular. |
Collaborative Prompting | Humans + AIs co-create in real time. | Boosts creativity and learning. |
Domain-Specific LLMs | Specialized models for law, medicine, and education. | New prompt niches & career paths. |
Regulated Prompt Auditing | Governments are tracking ethical AI usage. | More emphasis on compliance and transparency. |
Key Takeaways
Advanced prompting isn’t about fancy syntax — it’s about structured reasoning and context control.
Learn to think like an AI conductor, orchestrating prompts, memory, and roles.
Combine CoT + Reflection + Persona prompting for high-quality, human-like responses.
Keep ethics and transparency at the heart of your workflows.
Stay adaptable — what’s “advanced” today will be standard next year.
“The best prompt engineers in 2025 won’t just communicate with AI — they’ll co-create with it.”
Challenges and How to Overcome Common Mistakes in Prompt Engineering
Becoming a skilled prompt engineer isn’t about memorizing syntax — it’s about continuous improvement.
Even experienced professionals hit roadblocks. The key is learning how to debug, iterate, and evolve with the models.
Common Challenges (and How to Fix Them)
Challenge | Why It Happens | Quick Fix |
1. Vague or Unclear Prompts | Lack of context or missing details leads to generic answers. | Add background, structure, and tone. E.g., “Summarize this for an executive audience in 3 bullet points.” |
2. Overloaded Prompts | Asking too many questions at once. | Break into smaller sub-prompts or chain them. |
3. Model Hallucinations | AI invents data when uncertain. | Use RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) or external source grounding. |
4. Repetitive or Biased Outputs | Prompt lacks diversity or includes skewed examples. | Use neutral phrasing and randomize examples. |
5. Inconsistent Responses | Missing constraints or persona. | Prime the model with roles: “You’re a legal expert analyzing contracts…” |
6. Poor Evaluation Metrics | No systematic prompt testing. | Use tools like PromptLayer or LangSmith to track output quality. |
7. Ethical Blind Spots | Forgetting transparency or fairness. | Add ethical checkpoints and test for harmful bias. |
Pro Tip: Treat every prompt like a mini software program — test, debug, document, and improve.
How to Build a Feedback Loop for Continuous Learning
- Test your prompts across different models (GPT, Gemini, Claude).
- Measure consistency and clarity using scoring tools.
- Iterate one variable at a time — format, tone, or context.
- Document everything — results, observations, and learnings.
- Refine using prompt evaluation frameworks (TruLens, Guardrails AI).
“Good prompt engineers write prompts.
Great ones debug them.”
Final Summary: The Roadmap to AI Fluency
Let’s recap your journey from beginner to pro
Stage | Focus | Key Actions |
Learn | Understand NLP, Python, and prompt types | Study transformer basics, practice in playgrounds |
Build | Experiment and design structured prompts | Create a prompt library, test workflows |
Apply | Use LangChain, RAG, and API chaining | Build small AI tools and apps |
Showcase | Create your prompt portfolio | Publish 3–5 projects with documentation |
Evolve | Master advanced & ethical techniques | Explore CoT, multimodal, and agentic prompting |
“Prompt engineering is the new communication literacy.
Learn it, apply it, and lead in the age of AI.”
Conclusion: Your Journey From Learner to AI Collaborator
Prompt engineering is not just another tech buzzword — it’s the new digital literacy of our time. In an era where AI powers communication, creativity, and problem-solving, those who can craft precise prompts will shape how technology learns, reasons, and creates.
Becoming a prompt engineer isn’t about memorizing commands — it’s about thinking critically, experimenting consistently, and applying context intelligently. By following this roadmap, you’ll evolve from asking simple questions to designing complex AI workflows that produce real-world impact.
Whether you’re a student exploring AI, a professional upgrading your skills, or a curious learner building your first project, 2025 is your moment to start. Each prompt you write brings you closer to mastering how to collaborate with intelligence, not just command it.
“AI won’t replace people who use it wisely — it will empower those who learn to guide it.”
So, take that first step. Open a playground, write your first prompt, and begin building your future — one iteration, one idea, and one conversation at a time.
Key Takeaways: Prompt Engineering Roadmap 2025
- Prompt engineering is the language of AI. Learn to think with AI, not just talk to it.
- No coding required to start — begin with curiosity, clear goals, and simple prompts.
- Follow a 12-month learning roadmap to grow from beginner to professional.
- Use top tools like ChatGPT, LangChain, LlamaIndex, and PromptLayer for real projects.
- Stay future-ready — 2025 brings multi-agent systems, multimodal prompts, and ethical AI practices.
Action step: Start experimenting today — document your best prompts, build a small AI project, and share your results. Every experiment is a step toward becoming a true AI collaborator.
FAQ’S
Prompt engineering is the process of designing and refining instructions given to large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Gemini, or Claude. The goal is to guide AI to produce accurate, relevant, and ethical outputs.
In 2025, LLMs power most AI tools — from chatbots to code assistants. Prompt engineering gives professionals the ability to control, customize, and optimize these models without retraining them.
You’ll need
- Basic understanding of NLP and transformer models
- Python fundamentals (for APIs)
- Communication skills for clarity and structure
- Analytical mindset for testing prompts
- Awareness of AI ethics and bias
With consistent effort
- Beginner level: 2–3 months
- Intermediate level: 6 months
- Professional: 12 months+
Hands-on practice matters more than certificates.
Not initially. You can start with no-code tools like ChatGPT Playground, Brolly AI, or Notion AI.
Coding (especially Python) becomes useful for automation, chaining, and fine-tuning later.
- Instructional
- Socratic
- Priming (Role-based)
- Example-based (Few-shot)
- Chain-of-Thought (reasoning)
- Multimodal (text + image + audio)
Each serves different goals — clarity, creativity, or reasoning.
- Prompting: Changing how you ask the model.
- Fine-tuning: Changing how the model behaves by retraining it.
Prompting is faster, cheaper, and easier for most real-world use cases.
- ChatGPT Playground (testing prompts)
- Gemini Studio (multimodal prompts)
- PromptLayer (tracking experiments)
- LangChain (workflow chaining)
- Hugging Face Hub (open models)
- Spend 15–30 minutes writing and refining prompts.
- Compare results across GPT, Claude, and Gemini.
- Keep a prompt log of successful structures.
- Join communities on Reddit or Discord to share results.
11. What are “few-shot” and “zero-shot” prompts?
- Zero-shot: The model performs a task with no examples.
- Few-shot: You give 1–3 examples to teach a pattern.
Few-shot prompting boosts reliability in complex tasks like code or summarization.
CoT prompting encourages the model to reason step-by-step, improving accuracy for logic-based questions.
Example: “Let’s think through this logically…”
An advanced version of CoT — the model explores multiple reasoning paths before choosing the best one.
Useful for decision-making, planning, and creative brainstorming.
- Writing overly long or vague prompts
- Forgetting to specify tone or audience
- Not testing across multiple models
- Ignoring ethical implications
Fix: Keep prompts short, structured, and iterative.
- OpenAI Prompt Guide
- Google Cloud Prompt Engineering Overview
- LangChain Docs
- Stanford CS324 Course
- Build a public portfolio (Notion or GitHub).
- Document prompts + results.
- Share “before vs after” examples.
- Participate in AI hackathons or prompt competitions.
Region | Entry | Mid | Senior |
USA | $90K | $130K | $180K+ |
India | ₹8 LPA | ₹16 LPA | ₹25 LPA+ |
Europe | €70K | €110K | €150K+ |
- Tech & SaaS – OpenAI, Anthropic, Google
- Finance & LegalTech – Data summarization, compliance bots
- Healthcare & Education – AI tutoring, patient data analysis
- Marketing & Media – Content automation and campaign design
- Agentic prompting (multi-AI collaboration)
- Auto-prompt optimization (AI improving prompts)
- Prompt security (guardrail systems)
- Domain-specific LLMs (law, medicine, finance)
- Voice/video prompts (multimodal interfaces)
Follow a structured roadmap
- Learn prompt types (0–1 month)
- Practice and build projects (2–6 months)
- Create a portfolio + apply for gigs (6–12 months)
Start small — one clear prompt a day leads to big results.
